Advanced Motorized Turntable Controller
HARDWARE REQUIRED:
- PICUNO Microcontroller board
- 1 × 4x4 Button Matrix Module
- 1 × 5V Stepper Motor
- 1 × ULN2003 Driver Board
- 1 × 4xAA Battery Pack (For external supply)
- Jumper wires
- USB cable
DESCRIPTION:
This project creates an advanced controller for a motorized turntable. Using the 4x4 keypad, you can command the stepper motor to perform precise actions. You can enter a specific mode to move the motor an exact number of degrees, toggle continuous rotation, change direction, and return the motor to its home position. The Thonny IDE's Shell or Serial Monitor provides real-time feedback on the current mode, direction, position, and other statuses.
For C / Arduino IDE:
No external libraries required.
For Micropython / Thonny IDE:
stepper.py: The library file for the ULN2003 Stepper Motor driver, saved to the PICUNO board.
For C / Arduino IDE:
No external libraries required.
For Micropython / Thonny IDE:
stepper.py: The library file for the ULN2003 Stepper Motor driver, saved to the PICUNO board.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
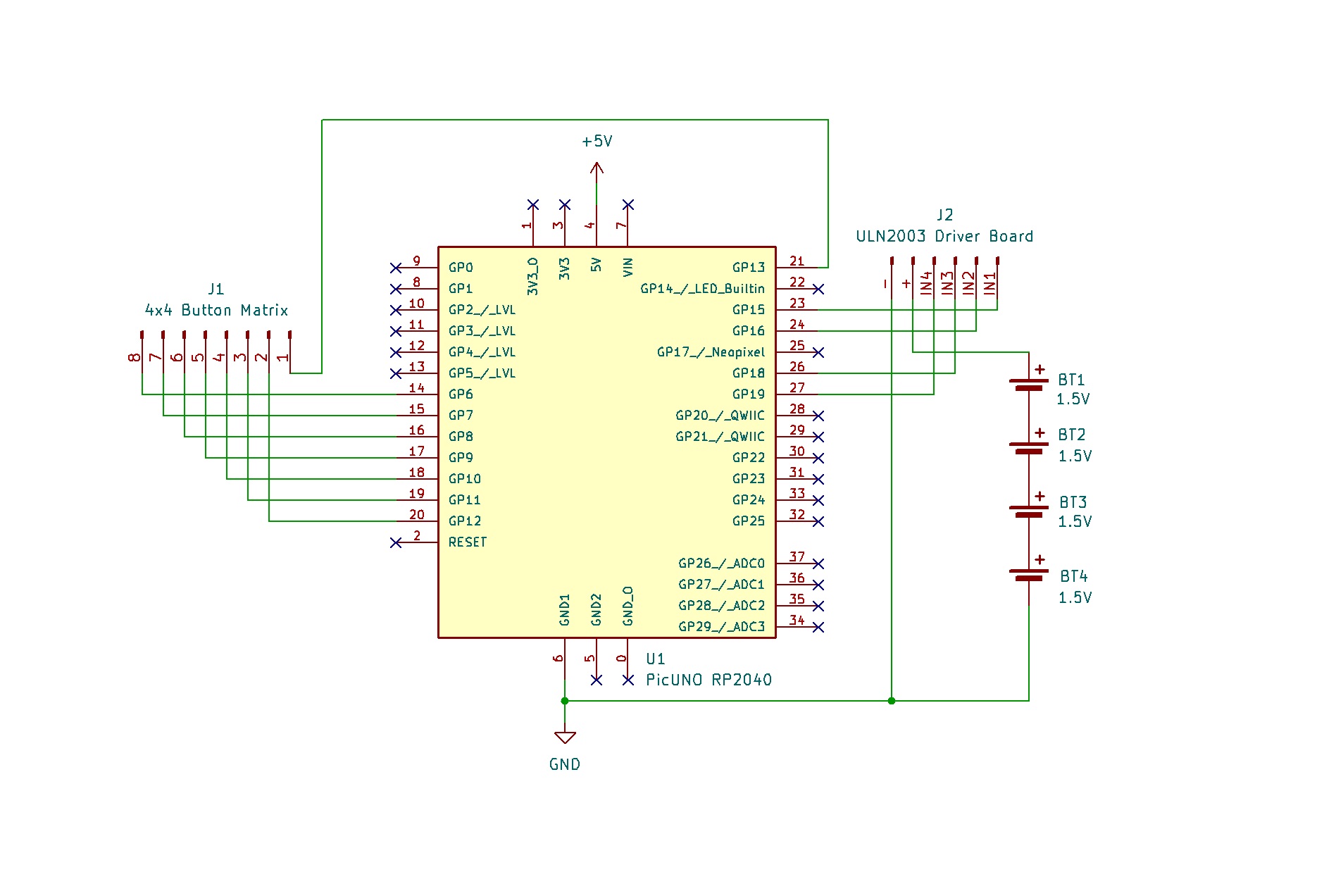
- Connect IN1, IN2, IN3, IN4 to PICUNO pins GPIO 15, 16, 18, and 19 respectively.
- Connect the driver's + and GND pins to positive terminal of the 4xAA Battery pack and GND respectively.
- Plug the stepper motor's connector into the socket on the driver board.
- Connect the negative terminal of the 4xAA Battery Pack to Common GND on breadboard.
- Connect the Row pins (5-8) to GPIO 6, 7, 8 and 9 respectively.
- Connect the Column pins (1-4) to GPIO 10, 11, 12 and 13 respectively.
SCHEMATIC:
ULN2003 Driver & Power:
ULN2003 IN1 → PICUNO GPIO 15
ULN2003 IN2 → PICUNO GPIO 16
ULN2003 IN3 → PICUNO GPIO 18
ULN2003 IN4 → PICUNO GPIO 19
ULN2003 Power + Pin → 4xAA Battery Pack (+)
ULN2003 Ground - Pin → GND
4x4 Button Matrix Module:
Pin 1 (Column 4) → GPIO 13
Pin 2 (Column 3) → GPIO 12
Pin 3 (Column 2) → GPIO 11
Pin 4 (Column 1) → GPIO 10
Pin 5 (Row 1) → GPIO 9
Pin 6 (Row 2) → GPIO 8
Pin 7 (Row 3) → GPIO 7
Pin 8 (Row 4) → GPIO 6
Common Ground Connection:
4xAA Battery Pack (-) → PICUNO Board GND
CODE -- C:
const int IN1 = 15;
const int IN2 = 16;
const int IN3 = 18;
const int IN4 = 19;
const byte ROWS = 4;
const byte COLS = 4;
byte rowPins[ROWS] = {6, 7, 8, 9};
byte colPins[COLS] = {10, 11, 12, 13};
char keys[ROWS][COLS] = {
{'1','2','3','A'},
{'4','5','6','B'},
{'7','8','9','C'},
{'*','0','#','D'}
};
const int stepsPerRevolution = 4096;
const int step_sequence[8][4] = {
{1, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 1}
};
int motor_pins[4] = {IN1, IN2, IN3, IN4};
int current_motor_step = 0;
// --- State Machine & Global Variables ---
enum Mode { MODE_IDLE, MODE_ANGLE };
Mode currentMode = MODE_IDLE;
String inputBuffer = "";
bool isRotating = false;
int direction = 1;
long currentPosition_steps = 0;
unsigned long lastStepTime = 0;
const int stepDelay = 2;
// --- Helper Functions ---
void stepMotor(int dir) {
current_motor_step += dir;
if (current_motor_step > 7) {
current_motor_step = 0;
}
if (current_motor_step < 0) {
current_motor_step = 7;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
digitalWrite(motor_pins[i], step_sequence[current_motor_step][i]);
}
}
void printStatus() {
String modeStr = (currentMode == MODE_ANGLE) ? "Angle" : "Direct";
String dirStr = (direction == 1) ? "CW" : "CCW";
String rotStr = (isRotating) ? "ON" : "OFF";
Serial.print("Mode: " + modeStr);
Serial.print(" | Dir: " + dirStr);
Serial.print(" | Rotate: " + rotStr);
Serial.print(" | Pos: ");
Serial.print(currentPosition_steps);
Serial.print(" | Input: [");
Serial.print(inputBuffer);
Serial.println("]");
}
void executeAngleCommand() {
if (inputBuffer.length() > 0) {
long degreesToMove = inputBuffer.toInt();
int stepsToMove = map(degreesToMove, 0, 360, 0, stepsPerRevolution);
Serial.print("--> Moving ");
Serial.print(degreesToMove);
Serial.println(" degrees...");
for (int i = 0; i < stepsToMove; i++) {
stepMotor(direction);
delay(stepDelay);
}
currentPosition_steps += (direction * stepsToMove);
Serial.println("--> Motion complete.");
}
}
void returnToHome() {
Serial.print("--> Returning to Home from position ");
Serial.print(currentPosition_steps);
Serial.println("...");
int homeDirection = (currentPosition_steps > 0) ? -1 : 1;
long stepsToHome = abs(currentPosition_steps);
for (long i = 0; i < stepsToHome; i++) {
stepMotor(homeDirection);
delay(stepDelay);
}
currentPosition_steps = 0;
Serial.println("--> At Home position.");
}
char scanKeypad() {
for (byte r = 0; r < ROWS; r++) {
digitalWrite(rowPins[r], LOW);
for (byte c = 0; c < COLS; c++) {
if (digitalRead(colPins[c]) == LOW) {
digitalWrite(rowPins[r], HIGH);
return keys[r][c];
}
}
digitalWrite(rowPins[r], HIGH);
}
return '\\0';
}
void handleKeyPress(char key) {
Serial.print("Key Pressed: '");
Serial.print(key);
Serial.println("'");
if (isDigit(key) && currentMode == MODE_ANGLE) {
inputBuffer += key;
} else {
switch (key) {
case 'A':
currentMode = MODE_ANGLE; isRotating = false; inputBuffer = "";
break;
case 'B':
returnToHome();
break;
case 'C':
direction *= -1;
break;
case 'D':
isRotating = !isRotating;
if (isRotating) { currentMode = MODE_IDLE; inputBuffer = ""; }
break;
case '*':
inputBuffer = "";
break;
case '#':
if (currentMode == MODE_ANGLE) {
executeAngleCommand();
inputBuffer = "";
currentMode = MODE_IDLE;
}
break;
}
}
printStatus();
}
// --- Main Program ---
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial);
// Configure Keypad Pins
for (byte r = 0; r < ROWS; r++) {
pinMode(rowPins[r], OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(rowPins[r], HIGH);
}
for (byte c = 0; c < COLS; c++) {
pinMode(colPins[c], INPUT_PULLUP);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
pinMode(motor_pins[i], OUTPUT);
}
Serial.println("--- Stepper Controller Ready ---");
printStatus();
}
char lastKeyState = '\\0';
unsigned long lastKeyPressTime = 0;
const long debounceDelay = 200;
void loop() {
if (isRotating && (millis() - lastStepTime >= stepDelay)) {
stepMotor(direction);
currentPosition_steps += direction;
lastStepTime = millis();
}
char currentKeyState = scanKeypad();
if (currentKeyState != lastKeyState) {
if (millis() - lastKeyPressTime > debounceDelay) {
if (currentKeyState != '\\0') {
handleKeyPress(currentKeyState);
}
lastKeyPressTime = millis();
}
}
lastKeyState = currentKeyState;
}
const int IN2 = 16;
const int IN3 = 18;
const int IN4 = 19;
const byte ROWS = 4;
const byte COLS = 4;
byte rowPins[ROWS] = {6, 7, 8, 9};
byte colPins[COLS] = {10, 11, 12, 13};
char keys[ROWS][COLS] = {
{'1','2','3','A'},
{'4','5','6','B'},
{'7','8','9','C'},
{'*','0','#','D'}
};
const int stepsPerRevolution = 4096;
const int step_sequence[8][4] = {
{1, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 1}
};
int motor_pins[4] = {IN1, IN2, IN3, IN4};
int current_motor_step = 0;
// --- State Machine & Global Variables ---
enum Mode { MODE_IDLE, MODE_ANGLE };
Mode currentMode = MODE_IDLE;
String inputBuffer = "";
bool isRotating = false;
int direction = 1;
long currentPosition_steps = 0;
unsigned long lastStepTime = 0;
const int stepDelay = 2;
// --- Helper Functions ---
void stepMotor(int dir) {
current_motor_step += dir;
if (current_motor_step > 7) {
current_motor_step = 0;
}
if (current_motor_step < 0) {
current_motor_step = 7;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
digitalWrite(motor_pins[i], step_sequence[current_motor_step][i]);
}
}
void printStatus() {
String modeStr = (currentMode == MODE_ANGLE) ? "Angle" : "Direct";
String dirStr = (direction == 1) ? "CW" : "CCW";
String rotStr = (isRotating) ? "ON" : "OFF";
Serial.print("Mode: " + modeStr);
Serial.print(" | Dir: " + dirStr);
Serial.print(" | Rotate: " + rotStr);
Serial.print(" | Pos: ");
Serial.print(currentPosition_steps);
Serial.print(" | Input: [");
Serial.print(inputBuffer);
Serial.println("]");
}
void executeAngleCommand() {
if (inputBuffer.length() > 0) {
long degreesToMove = inputBuffer.toInt();
int stepsToMove = map(degreesToMove, 0, 360, 0, stepsPerRevolution);
Serial.print("--> Moving ");
Serial.print(degreesToMove);
Serial.println(" degrees...");
for (int i = 0; i < stepsToMove; i++) {
stepMotor(direction);
delay(stepDelay);
}
currentPosition_steps += (direction * stepsToMove);
Serial.println("--> Motion complete.");
}
}
void returnToHome() {
Serial.print("--> Returning to Home from position ");
Serial.print(currentPosition_steps);
Serial.println("...");
int homeDirection = (currentPosition_steps > 0) ? -1 : 1;
long stepsToHome = abs(currentPosition_steps);
for (long i = 0; i < stepsToHome; i++) {
stepMotor(homeDirection);
delay(stepDelay);
}
currentPosition_steps = 0;
Serial.println("--> At Home position.");
}
char scanKeypad() {
for (byte r = 0; r < ROWS; r++) {
digitalWrite(rowPins[r], LOW);
for (byte c = 0; c < COLS; c++) {
if (digitalRead(colPins[c]) == LOW) {
digitalWrite(rowPins[r], HIGH);
return keys[r][c];
}
}
digitalWrite(rowPins[r], HIGH);
}
return '\\0';
}
void handleKeyPress(char key) {
Serial.print("Key Pressed: '");
Serial.print(key);
Serial.println("'");
if (isDigit(key) && currentMode == MODE_ANGLE) {
inputBuffer += key;
} else {
switch (key) {
case 'A':
currentMode = MODE_ANGLE; isRotating = false; inputBuffer = "";
break;
case 'B':
returnToHome();
break;
case 'C':
direction *= -1;
break;
case 'D':
isRotating = !isRotating;
if (isRotating) { currentMode = MODE_IDLE; inputBuffer = ""; }
break;
case '*':
inputBuffer = "";
break;
case '#':
if (currentMode == MODE_ANGLE) {
executeAngleCommand();
inputBuffer = "";
currentMode = MODE_IDLE;
}
break;
}
}
printStatus();
}
// --- Main Program ---
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial);
// Configure Keypad Pins
for (byte r = 0; r < ROWS; r++) {
pinMode(rowPins[r], OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(rowPins[r], HIGH);
}
for (byte c = 0; c < COLS; c++) {
pinMode(colPins[c], INPUT_PULLUP);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
pinMode(motor_pins[i], OUTPUT);
}
Serial.println("--- Stepper Controller Ready ---");
printStatus();
}
char lastKeyState = '\\0';
unsigned long lastKeyPressTime = 0;
const long debounceDelay = 200;
void loop() {
if (isRotating && (millis() - lastStepTime >= stepDelay)) {
stepMotor(direction);
currentPosition_steps += direction;
lastStepTime = millis();
}
char currentKeyState = scanKeypad();
if (currentKeyState != lastKeyState) {
if (millis() - lastKeyPressTime > debounceDelay) {
if (currentKeyState != '\\0') {
handleKeyPress(currentKeyState);
}
lastKeyPressTime = millis();
}
}
lastKeyState = currentKeyState;
}
step_sequence array - This 2D array holds the 8 specific ON/OFF patterns for the motor's four coils. Cycling through these patterns is what creates smooth rotation.
stepMotor() function - It advances one step in the sequence and directly sets the motor pins HIGH or LOW.
scanKeypad() function - This function manually scans the keypad's rows and columns to find which button is currently pressed.
pinMode(..., INPUT_PULLUP) - This command is essential for the manual scan. It activates an internal resistor in the Arduino, keeping the column pins HIGH until a pressed button pulls them LOW.
Non-Blocking Timers (millis()) - The code uses two separate timers based on millis(). One creates the steady pulse for continuous motor rotation, and the other handles the delay between key presses. This allows the motor to spin while the keypad is still responsive.
currentPosition_steps variable - This variable acts as a counter or "memory," tracking the motor's exact position relative to its starting point.
returnToHome() function - This function uses the currentPosition_steps variable to calculate the exact number of reverse steps needed to return the motor precisely to its zero position.
stepMotor() function - It advances one step in the sequence and directly sets the motor pins HIGH or LOW.
scanKeypad() function - This function manually scans the keypad's rows and columns to find which button is currently pressed.
pinMode(..., INPUT_PULLUP) - This command is essential for the manual scan. It activates an internal resistor in the Arduino, keeping the column pins HIGH until a pressed button pulls them LOW.
Non-Blocking Timers (millis()) - The code uses two separate timers based on millis(). One creates the steady pulse for continuous motor rotation, and the other handles the delay between key presses. This allows the motor to spin while the keypad is still responsive.
currentPosition_steps variable - This variable acts as a counter or "memory," tracking the motor's exact position relative to its starting point.
returnToHome() function - This function uses the currentPosition_steps variable to calculate the exact number of reverse steps needed to return the motor precisely to its zero position.
CODE -- PYTHON:
from machine import Pin, PWM
from time import sleep_ms, ticks_ms, ticks_diff
from stepper import Stepper
motor = Stepper(15, 16, 18, 19)
steps_per_revolution = 4096
keypad_map = [['1','2','3','A'],['4','5','6','B'],['7','8','9','C'],['*','0','#','D']]
row_pins = [Pin(pin, Pin.OUT) for pin in [6, 7, 8, 9]]
col_pins = [Pin(pin, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN) for pin in [10, 11, 12, 13]]
is_in_angle_mode = False
input_buffer = ""
is_rotating = False
direction = 1
currentPosition_steps = 0
# --- Timer variables ---
last_key_press_time = 0
last_step_time = 0
DEBOUNCE_DELAY_MS = 200
STEP_DELAY_MS = 2
# --- Helper Functions ---
def scan_keypad():
for r, row_pin in enumerate(row_pins):
row_pin.high()
for c, col_pin in enumerate(col_pins):
if col_pin.value() == 1:
row_pin.low()
return keypad_map[r][c]
row_pin.low()
return None
def execute_angle_command():
global currentPosition_steps
if input_buffer:
degrees_to_move = int(input_buffer)
steps_to_move = int((degrees_to_move / 360) * steps_per_revolution)
print(f"--> Moving {degrees_to_move} degrees...")
motor.step(steps_to_move, direction)
currentPosition_steps += (steps_to_move * direction)
print("--> Motion complete.")
def return_to_home():
global currentPosition_steps
print(f"--> Returning to Home from position {currentPosition_steps}...")
motor.step(-currentPosition_steps)
currentPosition_steps = 0
print("--> At Home position.")
def print_status():
mode_str = "Angle" if is_in_angle_mode else "Direct"
dir_str = "CW" if direction == 1 else "CCW"
rot_str = "ON" if is_rotating else "OFF"
print(f"Mode: {mode_str} | Dir: {dir_str} | Rotate: {rot_str} | Pos: {currentPosition_steps} | Input: [{input_buffer}]")
# --- Main Program ---
print("--- Stepper Controller Ready ---")
print_status()
last_key_state = None
while True:
if is_rotating and ticks_diff(ticks_ms(), last_step_time) >= STEP_DELAY_MS:
motor.step(1, direction)
currentPosition_steps += direction
last_step_time = ticks_ms()
current_key = scan_keypad()
if current_key and current_key != last_key_state:
if ticks_diff(ticks_ms(), last_key_press_time) > DEBOUNCE_DELAY_MS:
last_key_press_time = ticks_ms()
key = current_key
print(f"Key Pressed: '{key}'")
if key.isdigit() and is_in_angle_mode:
input_buffer += key
else:
if key == 'A':
is_in_angle_mode = True; is_rotating = False; input_buffer = ""
elif key == 'B':
return_to_home()
elif key == 'C':
direction *= -1
elif key == 'D':
is_in_angle_mode = False
is_rotating = not is_rotating
elif key == '*':
input_buffer = ""
elif key == '#':
if is_in_angle_mode:
execute_angle_command()
input_buffer = ""; is_in_angle_mode = False
print_status()
last_key_state = current_key
from time import sleep_ms, ticks_ms, ticks_diff
from stepper import Stepper
motor = Stepper(15, 16, 18, 19)
steps_per_revolution = 4096
keypad_map = [['1','2','3','A'],['4','5','6','B'],['7','8','9','C'],['*','0','#','D']]
row_pins = [Pin(pin, Pin.OUT) for pin in [6, 7, 8, 9]]
col_pins = [Pin(pin, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN) for pin in [10, 11, 12, 13]]
is_in_angle_mode = False
input_buffer = ""
is_rotating = False
direction = 1
currentPosition_steps = 0
# --- Timer variables ---
last_key_press_time = 0
last_step_time = 0
DEBOUNCE_DELAY_MS = 200
STEP_DELAY_MS = 2
# --- Helper Functions ---
def scan_keypad():
for r, row_pin in enumerate(row_pins):
row_pin.high()
for c, col_pin in enumerate(col_pins):
if col_pin.value() == 1:
row_pin.low()
return keypad_map[r][c]
row_pin.low()
return None
def execute_angle_command():
global currentPosition_steps
if input_buffer:
degrees_to_move = int(input_buffer)
steps_to_move = int((degrees_to_move / 360) * steps_per_revolution)
print(f"--> Moving {degrees_to_move} degrees...")
motor.step(steps_to_move, direction)
currentPosition_steps += (steps_to_move * direction)
print("--> Motion complete.")
def return_to_home():
global currentPosition_steps
print(f"--> Returning to Home from position {currentPosition_steps}...")
motor.step(-currentPosition_steps)
currentPosition_steps = 0
print("--> At Home position.")
def print_status():
mode_str = "Angle" if is_in_angle_mode else "Direct"
dir_str = "CW" if direction == 1 else "CCW"
rot_str = "ON" if is_rotating else "OFF"
print(f"Mode: {mode_str} | Dir: {dir_str} | Rotate: {rot_str} | Pos: {currentPosition_steps} | Input: [{input_buffer}]")
# --- Main Program ---
print("--- Stepper Controller Ready ---")
print_status()
last_key_state = None
while True:
if is_rotating and ticks_diff(ticks_ms(), last_step_time) >= STEP_DELAY_MS:
motor.step(1, direction)
currentPosition_steps += direction
last_step_time = ticks_ms()
current_key = scan_keypad()
if current_key and current_key != last_key_state:
if ticks_diff(ticks_ms(), last_key_press_time) > DEBOUNCE_DELAY_MS:
last_key_press_time = ticks_ms()
key = current_key
print(f"Key Pressed: '{key}'")
if key.isdigit() and is_in_angle_mode:
input_buffer += key
else:
if key == 'A':
is_in_angle_mode = True; is_rotating = False; input_buffer = ""
elif key == 'B':
return_to_home()
elif key == 'C':
direction *= -1
elif key == 'D':
is_in_angle_mode = False
is_rotating = not is_rotating
elif key == '*':
input_buffer = ""
elif key == '#':
if is_in_angle_mode:
execute_angle_command()
input_buffer = ""; is_in_angle_mode = False
print_status()
last_key_state = current_key
stepper.py library - A custom library used to simplify the 8-step sequence required to make the stepper motor turn.
scan_keypad() function - A non-blocking function that quickly scans the keypad for a press without pausing the program, which is essential for the continuous rotation to work smoothly.
is_in_angle_mode - A boolean variable that acts as a "state" for our program. It tracks whether the controller should be accepting numbers for an angle command or just listening for direct commands.
currentPosition_steps - A variable that acts as the motor's memory. It is updated every time the motor moves to keep a precise count of its current position relative to its start.
return_to_home() - The function for the 'B' button. It uses the currentPosition_steps variable to calculate the exact reverse motion needed to get back to the starting point.
Non-Blocking Timers (ticks_ms) - This logic is the key to the whole project. It allows the main loop to run very fast, handling both the perfectly-timed pulses for continuous rotation and instantly checking for keypad presses without either task interfering with the other.
scan_keypad() function - A non-blocking function that quickly scans the keypad for a press without pausing the program, which is essential for the continuous rotation to work smoothly.
is_in_angle_mode - A boolean variable that acts as a "state" for our program. It tracks whether the controller should be accepting numbers for an angle command or just listening for direct commands.
currentPosition_steps - A variable that acts as the motor's memory. It is updated every time the motor moves to keep a precise count of its current position relative to its start.
return_to_home() - The function for the 'B' button. It uses the currentPosition_steps variable to calculate the exact reverse motion needed to get back to the starting point.
Non-Blocking Timers (ticks_ms) - This logic is the key to the whole project. It allows the main loop to run very fast, handling both the perfectly-timed pulses for continuous rotation and instantly checking for keypad presses without either task interfering with the other.