Robot Choreographer

HARDWARE REQUIRED:
- PICUNO Microcontroller board
- 1 × 2-Wheel Chassis (with wheels, motors, etc.) full set
- 1 × 298N Motor Driver
- 1 × 4xAA Battery pack (with fresh or rechargeable batteries)
- 1 × 9V Battery (optional for external power supply to PICUNO)
- Jumper wires
- USB cable
DESCRIPTION:
This project turns the 2-wheel chassis into a "robot choreographer" that can perform a pre-programmed sequence of precise movements. The code contains high-level commands for actions like moving forward, turning, and spinning in place. The main program calls these functions in a sequence to execute a "dance routine," such as driving forward and backward, spinning 360 degrees, and tracing a perfect square on the floor. This project teaches the fundamentals of differential steering, which is the core concept behind how two-wheeled robots navigate and turn.
ASSEMBLY OF 2-WHEEL CHASIS KIT:
1.) Prepare the Chassis: If your chassis parts are acrylic, they often come with a protective paper or plastic film. Peel this film off all the pieces.
2.) Mount the Motors: Attach the two yellow DC motors to the main chassis plate. Use the brackets and long screws/nuts that came with the kit to secure them firmly in place.
3.) Attach the Wheels: Push the two main wheels onto the plastic shafts of the motors. They should be a snug fit.
4.) Attach the Caster Wheel: Mount the third, free-spinning wheel (the caster or ball wheel) to the other end of the chassis. This wheel acts as the front or back support and allows the robot to turn easily.
5.) Mount the Battery Holder: Use screws to attach the 4xAA battery pack at the bottom of the chassis.
6.) Mount the Electronics: Finally, mount the PICUNO and the L298N motor driver board onto the chassis, usually using screws/double tape. Position them such that to easily run wires to the motors.
ASSEMBLY OF 2-WHEEL CHASIS KIT:
1.) Prepare the Chassis: If your chassis parts are acrylic, they often come with a protective paper or plastic film. Peel this film off all the pieces.
2.) Mount the Motors: Attach the two yellow DC motors to the main chassis plate. Use the brackets and long screws/nuts that came with the kit to secure them firmly in place.
3.) Attach the Wheels: Push the two main wheels onto the plastic shafts of the motors. They should be a snug fit.
4.) Attach the Caster Wheel: Mount the third, free-spinning wheel (the caster or ball wheel) to the other end of the chassis. This wheel acts as the front or back support and allows the robot to turn easily.
5.) Mount the Battery Holder: Use screws to attach the 4xAA battery pack at the bottom of the chassis.
6.) Mount the Electronics: Finally, mount the PICUNO and the L298N motor driver board onto the chassis, usually using screws/double tape. Position them such that to easily run wires to the motors.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
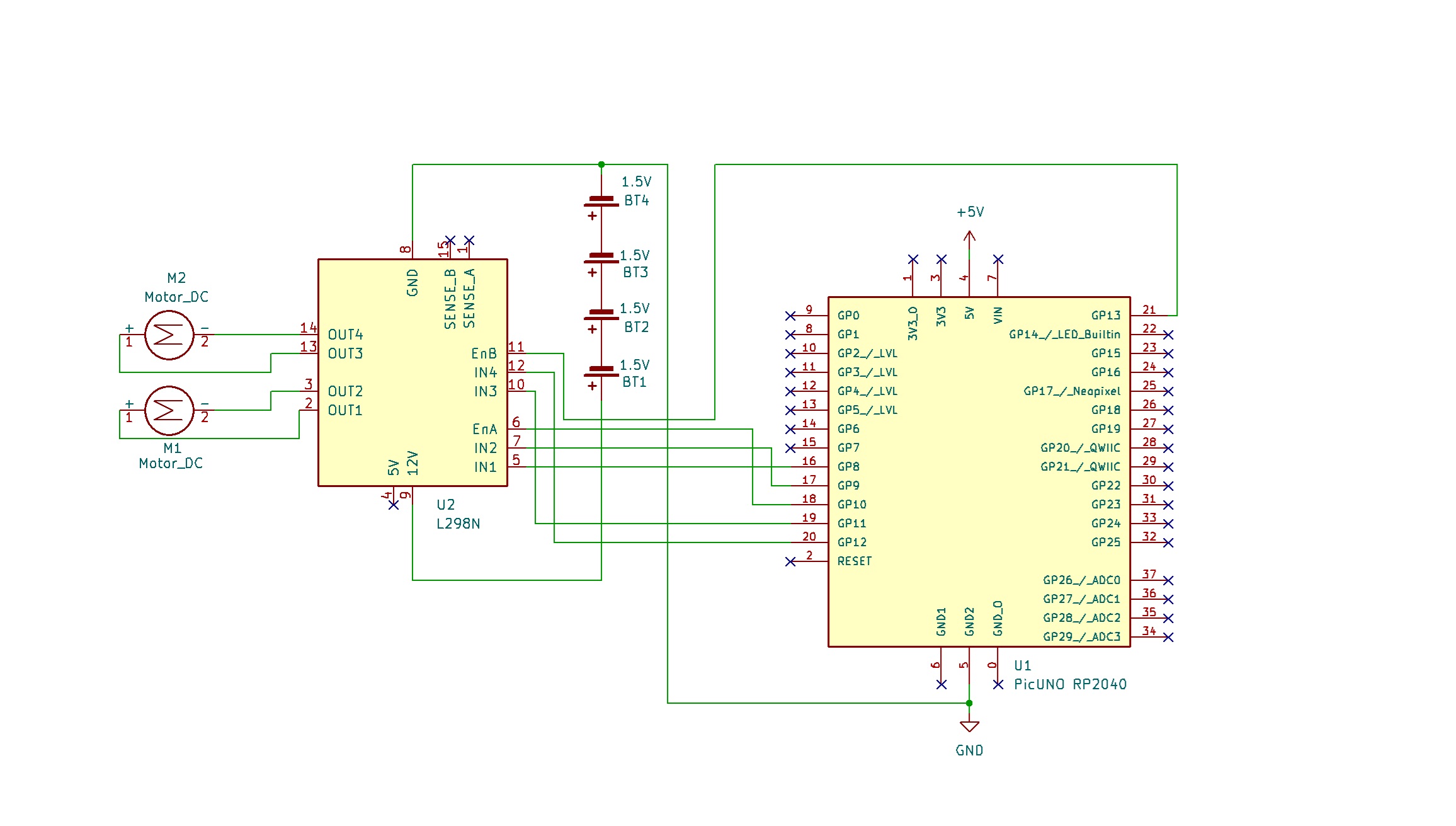
- OUT1 & OUT2: Connect these two screw terminals to the outputs for the first motor (e.g., the left wheel). Connect the two wires from one DC motor here.
- OUT3 & OUT4: Connect these two screw terminals to the outputs for the second motor (e.g., the right wheel). Connect the two wires from the other DC motor here.
- Connect the positive terminal (+) of the 4xAA battery pack to the 12V screw terminal.
- Connect the negative terminal (-) of the 4xAA battery pack to the GND screw terminal.
- Also connect the GND terminal on the L298N to a GND pin on the microcontroller to create a common ground.
- Connect the IN1 pin (Left motor) to GPIO 8.
- Connect the IN2 pin (Left motor) to GPIO 9.
- Connect the ENA pin (Left motor speed) to GPIO 10.
- Connect the IN1 pin (Right motor) to GPIO 11.
- Connect the IN2 pin (Right motor) to GPIO 12.
- Connect the ENB pin (Right motor speed) to GPIO 13.
NOTE: Remove the ENA and ENB jumpers on the L298N motor driver.
OPTIONAL: You can power the PICUNO using an external power supply (9V Battery) through DC Jack, once you have uploaded the code to the microcontroller.
SCHEMATIC:
L298N Motor Driver:
OUT2 & OUT2 → Outputs for the Left Motor.
OUT3 & OUT4 → Outputs for the Right Motor.
12V → positive terminal (+) of 4xAA battery pack.
GND → negative terminal (-) of 4xAA battery pack → GND on PICUNO.
IN1 (Left Motor) → GPIO 8
IN2 (Left Motor) → GPIO 9
ENA (Left Motor speed) → GPIO 10
IN3 (Right Motor) → GPIO 11
IN4 (Right Motor) → GPIO 12
ENB (Right Motor) → GPIO 13
CODE -- C:
const int L_IN1_PIN = 8, L_IN2_PIN = 9, L_ENA_PIN = 10;
const int R_IN3_PIN = 11, R_IN4_PIN = 12, R_ENB_PIN = 13;
void setup() {
pinMode(L_IN1_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(L_IN2_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(L_ENA_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(R_IN3_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(R_IN4_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(R_ENB_PIN, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
// --- Helper Function for Raw Motor Control ---
void setMotorSpeed(char motor, int speed) {
int duty = map(abs(speed), 0, 100, 0, 255);
if (motor == 'L') {
if (speed > 0) {
digitalWrite(L_IN1_PIN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(L_IN2_PIN, LOW);
}
else if (speed < 0) {
digitalWrite(L_IN1_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(L_IN2_PIN, HIGH);
}
else {
digitalWrite(L_IN1_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(L_IN2_PIN, LOW);
}
analogWrite(L_ENA_PIN, duty);
}
else if (motor == 'R') {
if (speed > 0) {
digitalWrite(R_IN3_PIN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(R_IN4_PIN, LOW);
}
else if (speed < 0) {
digitalWrite(R_IN3_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(R_IN4_PIN, HIGH);
}
else {
digitalWrite(R_IN3_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(R_IN4_PIN, LOW);
}
analogWrite(R_ENB_PIN, duty);
}
}
// --- High-Level Movement Functions ---
void forward(int speed = 80) {
setMotorSpeed('L', speed);
setMotorSpeed('R', speed);
}
void backward(int speed = 80) {
setMotorSpeed('L', -speed);
setMotorSpeed('R', -speed);
}
void stopMotors() {
setMotorSpeed('L', 0);
setMotorSpeed('R', 0);
}
void turn_right(int speed = 70) {
setMotorSpeed('L', speed);
setMotorSpeed('R', 0);
}
void spin_in_place(int speed = 60) {
setMotorSpeed('L', speed);
setMotorSpeed('R', -speed);
}
void loop() {
Serial.println("Starting robot dance routine...");
delay(2000);
// 1. Drive forward and backward
Serial.println("Part 1: Forward and Backward");
forward();
delay(1000);
backward();
delay(1000);
stopMotors();
delay(1000);
// 2. Spin in place
Serial.println("Part 2: Spinning");
spin_in_place();
delay(3600); // Adjust this time for a full 360 spin
stopMotors();
delay(1000);
// 3. Drive in a square
Serial.println("Part 3: Driving in a square");
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
Serial.print(" Side ");
Serial.println(i + 1);
forward();
delay(1000);
turn_right();
delay(700); // Adjust this time for a perfect 90-degree turn
}
stopMotors();
Serial.println("Dance complete. Restarting in 5 seconds...");
delay(5000);
}
const int R_IN3_PIN = 11, R_IN4_PIN = 12, R_ENB_PIN = 13;
void setup() {
pinMode(L_IN1_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(L_IN2_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(L_ENA_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(R_IN3_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(R_IN4_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(R_ENB_PIN, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
// --- Helper Function for Raw Motor Control ---
void setMotorSpeed(char motor, int speed) {
int duty = map(abs(speed), 0, 100, 0, 255);
if (motor == 'L') {
if (speed > 0) {
digitalWrite(L_IN1_PIN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(L_IN2_PIN, LOW);
}
else if (speed < 0) {
digitalWrite(L_IN1_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(L_IN2_PIN, HIGH);
}
else {
digitalWrite(L_IN1_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(L_IN2_PIN, LOW);
}
analogWrite(L_ENA_PIN, duty);
}
else if (motor == 'R') {
if (speed > 0) {
digitalWrite(R_IN3_PIN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(R_IN4_PIN, LOW);
}
else if (speed < 0) {
digitalWrite(R_IN3_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(R_IN4_PIN, HIGH);
}
else {
digitalWrite(R_IN3_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(R_IN4_PIN, LOW);
}
analogWrite(R_ENB_PIN, duty);
}
}
// --- High-Level Movement Functions ---
void forward(int speed = 80) {
setMotorSpeed('L', speed);
setMotorSpeed('R', speed);
}
void backward(int speed = 80) {
setMotorSpeed('L', -speed);
setMotorSpeed('R', -speed);
}
void stopMotors() {
setMotorSpeed('L', 0);
setMotorSpeed('R', 0);
}
void turn_right(int speed = 70) {
setMotorSpeed('L', speed);
setMotorSpeed('R', 0);
}
void spin_in_place(int speed = 60) {
setMotorSpeed('L', speed);
setMotorSpeed('R', -speed);
}
void loop() {
Serial.println("Starting robot dance routine...");
delay(2000);
// 1. Drive forward and backward
Serial.println("Part 1: Forward and Backward");
forward();
delay(1000);
backward();
delay(1000);
stopMotors();
delay(1000);
// 2. Spin in place
Serial.println("Part 2: Spinning");
spin_in_place();
delay(3600); // Adjust this time for a full 360 spin
stopMotors();
delay(1000);
// 3. Drive in a square
Serial.println("Part 3: Driving in a square");
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
Serial.print(" Side ");
Serial.println(i + 1);
forward();
delay(1000);
turn_right();
delay(700); // Adjust this time for a perfect 90-degree turn
}
stopMotors();
Serial.println("Dance complete. Restarting in 5 seconds...");
delay(5000);
}
setMotorSpeed() function - Using Arduino's digitalWrite() for direction and analogWrite() for speed.
analogWrite() - This is the command for sending a PWM signal. It uses a value from 0 (off) to 255 (100% speed). The map() function is used to convert the 0-100 speed percentage to this 0-255 range.
High-Level Functions - Functions like forward() and spin_in_place() are created to make the main loop() easier to read and understand.
loop() - The loop() function in Arduino is naturally infinite. The entire choreography sequence is placed inside it and will repeat after a 5-second pause.
analogWrite() - This is the command for sending a PWM signal. It uses a value from 0 (off) to 255 (100% speed). The map() function is used to convert the 0-100 speed percentage to this 0-255 range.
High-Level Functions - Functions like forward() and spin_in_place() are created to make the main loop() easier to read and understand.
loop() - The loop() function in Arduino is naturally infinite. The entire choreography sequence is placed inside it and will repeat after a 5-second pause.
CODE -- PYTHON:
from machine import Pin, PWM
from time import sleep
# Left Motor
L_IN1_PIN = 8
L_IN2_PIN = 9
L_ENA_PIN = 10
# Right Motor
R_IN3_PIN = 11
R_IN4_PIN = 12
R_ENB_PIN = 13
# Left Motor
L_IN1 = Pin(L_IN1_PIN, Pin.OUT)
L_IN2 = Pin(L_IN2_PIN, Pin.OUT)
L_ENA = PWM(Pin(L_ENA_PIN))
L_ENA.freq(1000)
# Right Motor
R_IN3 = Pin(R_IN3_PIN, Pin.OUT)
R_IN4 = Pin(R_IN4_PIN, Pin.OUT)
R_ENB = PWM(Pin(R_ENB_PIN))
R_ENB.freq(1000)
# --- Helper Function for Raw Motor Control ---
def set_motor_speed(motor, speed):
"""Sets motor speed. speed is from -100 to 100."""
duty = int(abs(speed) / 100 * 65535)
if motor == 'left':
if speed > 0: L_IN1.high(); L_IN2.low() # Forward
elif speed < 0: L_IN1.low(); L_IN2.high() # Backward
else: L_IN1.low(); L_IN2.low() # Stop
L_ENA.duty_u16(duty)
elif motor == 'right':
if speed > 0: R_IN3.high(); R_IN4.low() # Forward
elif speed < 0: R_IN3.low(); R_IN4.high() # Backward
else: R_IN3.low(); R_IN4.low() # Stop
R_ENB.duty_u16(duty)
# --- High-Level Movement Functions ---
def forward(speed=80):
set_motor_speed('left', speed)
set_motor_speed('right', speed)
def backward(speed=80):
set_motor_speed('left', -speed)
set_motor_speed('right', -speed)
def stop():
set_motor_speed('left', 0)
set_motor_speed('right', 0)
def turn_left(speed=70):
"""Pivots around the left wheel."""
set_motor_speed('left', 0)
set_motor_speed('right', speed)
def turn_right(speed=70):
"""Pivots around the right wheel."""
set_motor_speed('left', speed)
set_motor_speed('right', 0)
def spin_in_place(speed=60):
"""Spins clockwise on the spot."""
set_motor_speed('left', speed)
set_motor_speed('right', -speed)
# --- Main "Choreography" Sequence ---
print("Starting robot dance routine...")
sleep(2)
while True:
# 1. Drive forward and backward
print("Part 1: Forward and Backward")
forward()
sleep(1)
backward()
sleep(1)
stop()
sleep(1)
#2. Spin in place
print("Part 2: Spinning")
spin_in_place()
sleep(3.6) # Adjust this time for a full 360 spin
stop()
sleep(1)
# 3. Drive in a square
print("Part 3: Driving in a square")
for i in range(4):
print(f" Side {i+1}")
forward()
sleep(1)
turn_right()
sleep(0.7) # Adjust this time for a perfect 90-degree turn
stop()
print("Dance complete.Restarting in 5 seconds...")
sleep(5)
from time import sleep
# Left Motor
L_IN1_PIN = 8
L_IN2_PIN = 9
L_ENA_PIN = 10
# Right Motor
R_IN3_PIN = 11
R_IN4_PIN = 12
R_ENB_PIN = 13
# Left Motor
L_IN1 = Pin(L_IN1_PIN, Pin.OUT)
L_IN2 = Pin(L_IN2_PIN, Pin.OUT)
L_ENA = PWM(Pin(L_ENA_PIN))
L_ENA.freq(1000)
# Right Motor
R_IN3 = Pin(R_IN3_PIN, Pin.OUT)
R_IN4 = Pin(R_IN4_PIN, Pin.OUT)
R_ENB = PWM(Pin(R_ENB_PIN))
R_ENB.freq(1000)
# --- Helper Function for Raw Motor Control ---
def set_motor_speed(motor, speed):
"""Sets motor speed. speed is from -100 to 100."""
duty = int(abs(speed) / 100 * 65535)
if motor == 'left':
if speed > 0: L_IN1.high(); L_IN2.low() # Forward
elif speed < 0: L_IN1.low(); L_IN2.high() # Backward
else: L_IN1.low(); L_IN2.low() # Stop
L_ENA.duty_u16(duty)
elif motor == 'right':
if speed > 0: R_IN3.high(); R_IN4.low() # Forward
elif speed < 0: R_IN3.low(); R_IN4.high() # Backward
else: R_IN3.low(); R_IN4.low() # Stop
R_ENB.duty_u16(duty)
# --- High-Level Movement Functions ---
def forward(speed=80):
set_motor_speed('left', speed)
set_motor_speed('right', speed)
def backward(speed=80):
set_motor_speed('left', -speed)
set_motor_speed('right', -speed)
def stop():
set_motor_speed('left', 0)
set_motor_speed('right', 0)
def turn_left(speed=70):
"""Pivots around the left wheel."""
set_motor_speed('left', 0)
set_motor_speed('right', speed)
def turn_right(speed=70):
"""Pivots around the right wheel."""
set_motor_speed('left', speed)
set_motor_speed('right', 0)
def spin_in_place(speed=60):
"""Spins clockwise on the spot."""
set_motor_speed('left', speed)
set_motor_speed('right', -speed)
# --- Main "Choreography" Sequence ---
print("Starting robot dance routine...")
sleep(2)
while True:
# 1. Drive forward and backward
print("Part 1: Forward and Backward")
forward()
sleep(1)
backward()
sleep(1)
stop()
sleep(1)
#2. Spin in place
print("Part 2: Spinning")
spin_in_place()
sleep(3.6) # Adjust this time for a full 360 spin
stop()
sleep(1)
# 3. Drive in a square
print("Part 3: Driving in a square")
for i in range(4):
print(f" Side {i+1}")
forward()
sleep(1)
turn_right()
sleep(0.7) # Adjust this time for a perfect 90-degree turn
stop()
print("Dance complete.Restarting in 5 seconds...")
sleep(5)
High-Level Movement Functions - Functions like forward(), turn_left(), and spin_in_place() translate simple commands into the specific wheel movements needed.
Differential Steering - The turn_right() function works by keeping the right wheel still and moving the left wheel forward. The spin_in_place() function works by moving the wheels in opposite directions. This is the core concept of differential steering.
set_motor_speed() function - This is the low-level function that controls the direction pins (IN1/IN2) and sets the speed using PWM (duty_u16).
Calibration - The sleep() values in the main sequence, especially for turning, must be adjusted to match your robot's specific motors and surface to achieve perfect 90-degree turns.
Differential Steering - The turn_right() function works by keeping the right wheel still and moving the left wheel forward. The spin_in_place() function works by moving the wheels in opposite directions. This is the core concept of differential steering.
set_motor_speed() function - This is the low-level function that controls the direction pins (IN1/IN2) and sets the speed using PWM (duty_u16).
Calibration - The sleep() values in the main sequence, especially for turning, must be adjusted to match your robot's specific motors and surface to achieve perfect 90-degree turns.