Joystick Status Display Using LCD
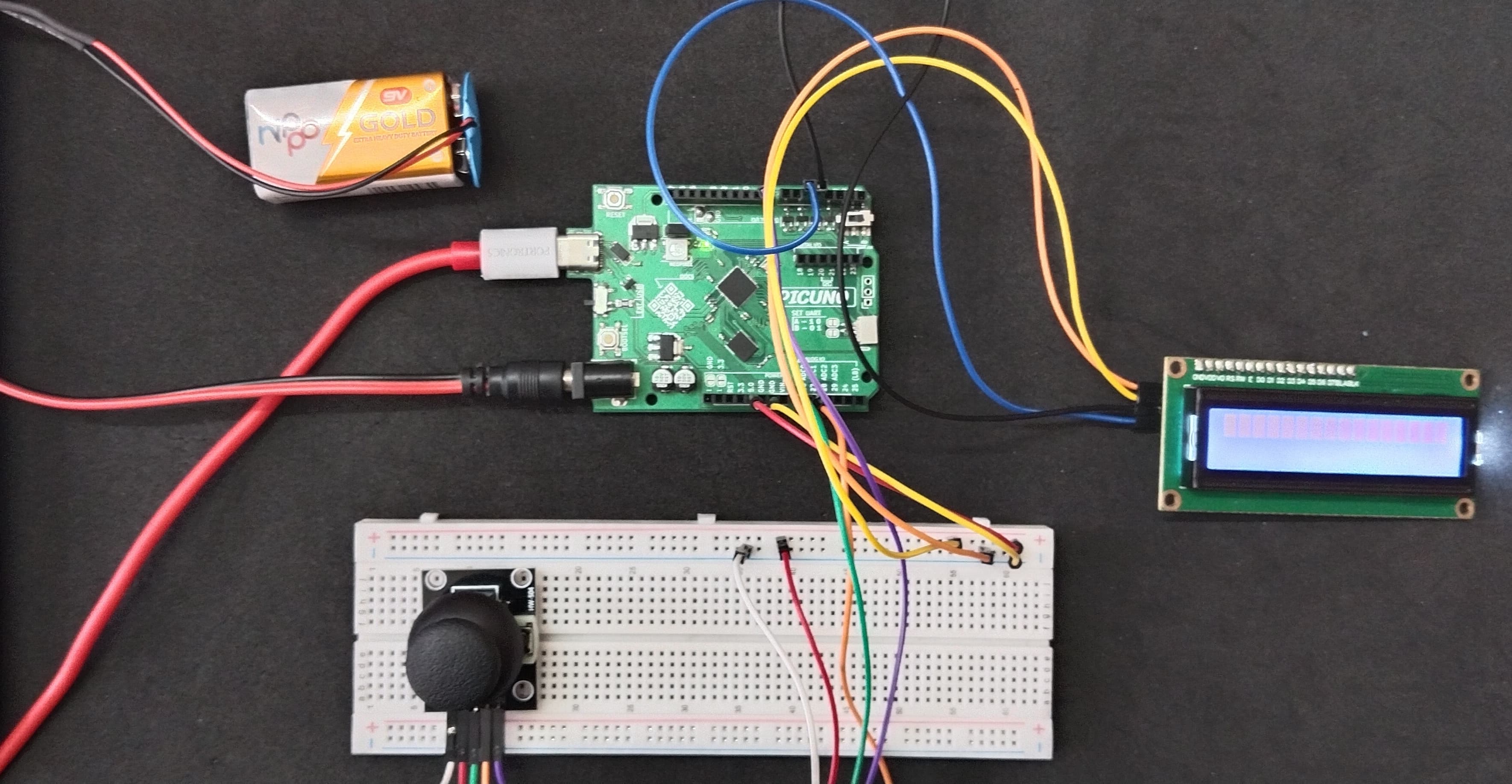
HARDWARE REQUIRED:
- PICUNO Microcontroller board
- 1 × 16x2 I2C LCD Display
- 1 × HW-504 Joystick Module
- Jumper wires
- USB cable
- 9V Battery with a snap connector (to power the board via the DC Jack)
DESCRIPTION:
This project creates a simple but powerful user interface by reading all the inputs from a Joystick XY module and displaying them in real-time. The program continuously reads the Analog values from the X and Y axes to get a 2D coordinate, as well as the digital state of the built-in push-button. This data is then formatted and sent to a 16x2 I2C LCD screen for immediate feedback. This project serves as a fundamental building block for any system that requires user control, such as games, navigation menus, or robot controllers.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
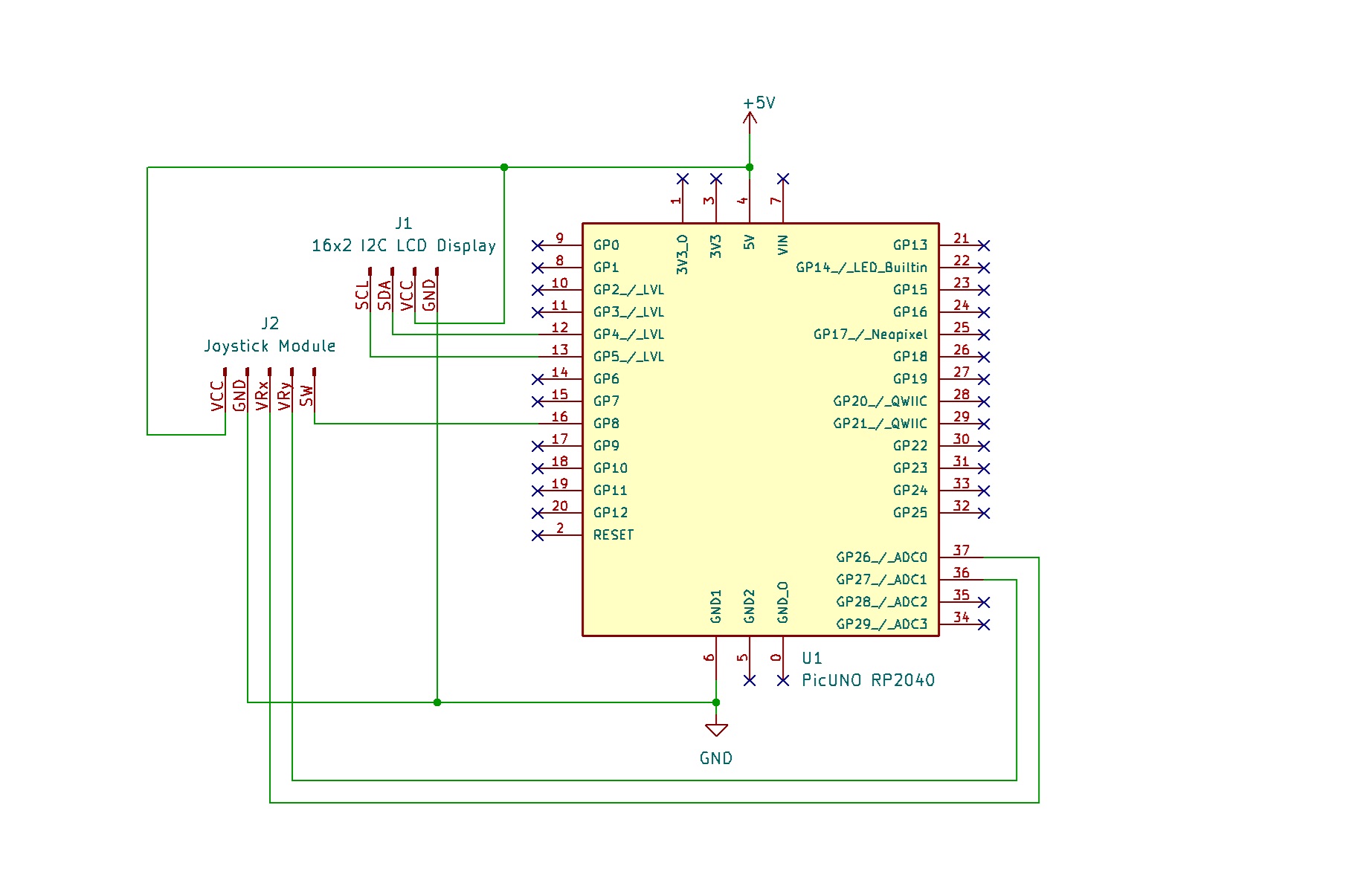
- Connect the LCD Module's GND pin to a GND pin on board.
- Connect the LCD Module's VCC pin to the 5V pin on board.
- Connect the LCD Module's SDA pin GPIO 4 (SDA Pin on PICUNO).
- Connect the LCD Module's SCL pin GPIO 5 (SCL Pin on PICUNO).
- JOYSTICK MODULE:
- Connect the VCC pin to 5V pin on the board.
- Connect the GND pin to GND pin on board.
- Connect the VRx pin to Analog Pin A0 (GPIO 26).
- Connect the VRy pin to Analog Pin A1 (GPIO 27).
- Connect the SW (Switch) pin to GPIO 8.
SCHEMATIC:
LCD VCC → 5V
LCD GND → GND
LCD SDA → GPIO 4 (Board SDA Pin)
LCD SCL → GPIO 5 (Board SCL Pin)
Joystick Module:
VCC → 5V
GND → GND
VRx → A0
VRy → A1
SW → GPIO 8
CODE -- C:
#include <Wire.h>
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h>
// Pin Definitions
const int JOY_X_PIN = A0;
const int JOY_Y_PIN = A1;
const int JOY_SW_PIN = 8;
// LCD Setup
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x27, 16, 2);
void setup() {
pinMode(JOY_SW_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP);
lcd.init();
lcd.backlight();
lcd.print("Joystick Test");
delay(1000);
}
void loop() {
// Read the values from the joystick
int xValue = analogRead(JOY_X_PIN);
int yValue = analogRead(JOY_Y_PIN);
int swValue = digitalRead(JOY_SW_PIN);
// Clear the screen and display values
lcd.clear();
// Display X and Y values on the top line
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("X:");
lcd.print(xValue);
lcd.setCursor(8, 0);
lcd.print("Y:");
lcd.print(yValue);
// Display the button state on the bottom line
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print("Switch: ");
if (swValue == LOW) { // LOW means pressed because of INPUT_PULLUP
lcd.print("Pressed");
} else {
lcd.print("Off");
}
delay(200);
}
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h>
// Pin Definitions
const int JOY_X_PIN = A0;
const int JOY_Y_PIN = A1;
const int JOY_SW_PIN = 8;
// LCD Setup
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x27, 16, 2);
void setup() {
pinMode(JOY_SW_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP);
lcd.init();
lcd.backlight();
lcd.print("Joystick Test");
delay(1000);
}
void loop() {
// Read the values from the joystick
int xValue = analogRead(JOY_X_PIN);
int yValue = analogRead(JOY_Y_PIN);
int swValue = digitalRead(JOY_SW_PIN);
// Clear the screen and display values
lcd.clear();
// Display X and Y values on the top line
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("X:");
lcd.print(xValue);
lcd.setCursor(8, 0);
lcd.print("Y:");
lcd.print(yValue);
// Display the button state on the bottom line
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print("Switch: ");
if (swValue == LOW) { // LOW means pressed because of INPUT_PULLUP
lcd.print("Pressed");
} else {
lcd.print("Off");
}
delay(200);
}
pinMode(JOY_SW_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP); - Configures the joystick's button pin as an input and enables an internal resistor to keep the signal stable.
analogRead(JOY_X_PIN) - Reads the joystick's position on one axis as a value from 0-1023.
digitalRead(JOY_SW_PIN) - Reads the state of the button. Because we are using INPUT_PULLUP, the value will be LOW when pressed.
lcd.setCursor(col, row) - This command is used to precisely position the text on the screen before printing.
analogRead(JOY_X_PIN) - Reads the joystick's position on one axis as a value from 0-1023.
digitalRead(JOY_SW_PIN) - Reads the state of the button. Because we are using INPUT_PULLUP, the value will be LOW when pressed.
lcd.setCursor(col, row) - This command is used to precisely position the text on the screen before printing.
CODE -- PYTHON:
from machine import Pin, ADC, I2C
from i2c_lcd import I2cLcd
from time import sleep
adc_x = ADC(Pin(26)) # A0
adc_y = ADC(Pin(27)) # A1
# Setup Digital pin for Joystick Switch
button = Pin(8, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)
i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4))
lcd = I2cLcd(i2c, 0x27, 2, 16)
lcd.putstr("Joystick Test")
sleep(1)
lcd.clear()
while True:
# Read all the values
x_val = adc_x.read_u16()
y_val = adc_y.read_u16()
sw_val = button.value()
# Format the text for display
x_text = f"X:{x_val:<5}" # Format X value
y_text = f"Y:{y_val:<5}" # Format Y value
sw_text = f"Switch: {'Pressed' if sw_val == 0 else 'Off'}"
# Display on the LCD
lcd.move_to(0, 0)
lcd.putstr(f"{x_text} {y_text}")
lcd.move_to(0, 1)
lcd.putstr(f"{sw_text:<16}")
sleep(0.2)
from i2c_lcd import I2cLcd
from time import sleep
adc_x = ADC(Pin(26)) # A0
adc_y = ADC(Pin(27)) # A1
# Setup Digital pin for Joystick Switch
button = Pin(8, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)
i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4))
lcd = I2cLcd(i2c, 0x27, 2, 16)
lcd.putstr("Joystick Test")
sleep(1)
lcd.clear()
while True:
# Read all the values
x_val = adc_x.read_u16()
y_val = adc_y.read_u16()
sw_val = button.value()
# Format the text for display
x_text = f"X:{x_val:<5}" # Format X value
y_text = f"Y:{y_val:<5}" # Format Y value
sw_text = f"Switch: {'Pressed' if sw_val == 0 else 'Off'}"
# Display on the LCD
lcd.move_to(0, 0)
lcd.putstr(f"{x_text} {y_text}")
lcd.move_to(0, 1)
lcd.putstr(f"{sw_text:<16}")
sleep(0.2)
adc_x = ADC(Pin(26)) - Creates an Analog-to-Digital Converter object for the X-axis pin.
button = Pin(8, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP) - Configures the button pin as an input with an internal pull-up resistor.
x_val = adc_x.read_u16() - Reads the joystick's X-axis position as a 16-bit value (0-65535).
sw_text = f"Switch: {'Pressed' if sw_val == 0 else 'Off'}" - This is a conditional expression (ternary operator) inside an f-string. It neatly formats the button status into the correct string in one line.
lcd.putstr(...) - Prints the final formatted strings to the LCD screen.
button = Pin(8, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP) - Configures the button pin as an input with an internal pull-up resistor.
x_val = adc_x.read_u16() - Reads the joystick's X-axis position as a 16-bit value (0-65535).
sw_text = f"Switch: {'Pressed' if sw_val == 0 else 'Off'}" - This is a conditional expression (ternary operator) inside an f-string. It neatly formats the button status into the correct string in one line.
lcd.putstr(...) - Prints the final formatted strings to the LCD screen.