Morse Code IR Transmitter
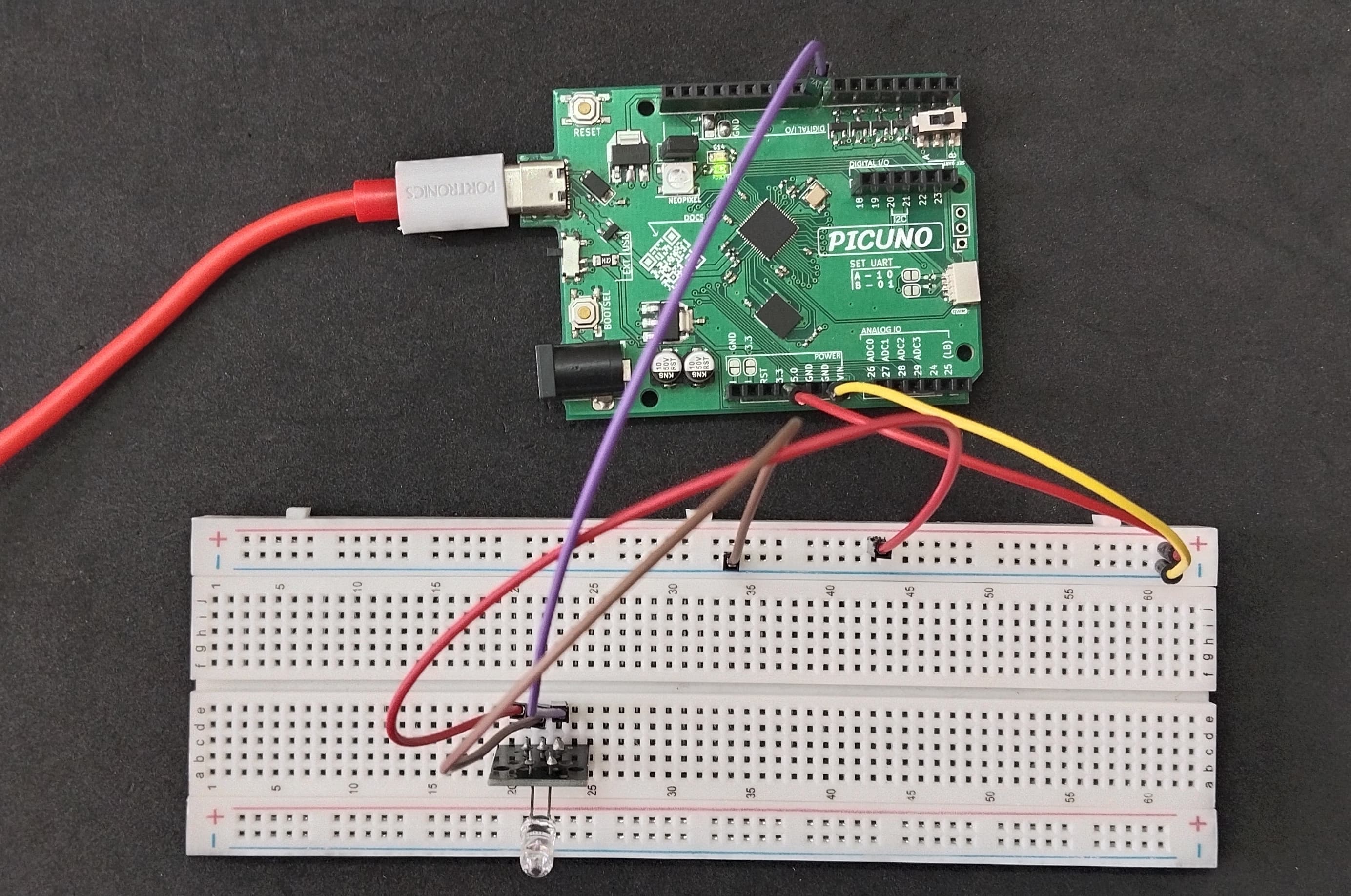
HARDWARE REQUIRED:
- PICUNO Microcontroller board
- 1 × HW-489 TR Emission Module
- Jumper wires
- USB cable
DESCRIPTION:
This project creates a transmitter that converts text into International Morse Code and sends it as a series of long and short flashes of invisible infrared light. The user can type a message into the Serial Monitor, and the microcontroller will look up each character, translate it to the corresponding dot-dash pattern, and transmit it with precise timing. The transmitted signal can be seen using any smartphone camera, demonstrating the principles of data encoding and wireless signal transmission.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:

- Connect the GND pin (-) of the IR Emitter module to GND on PICUNO.
- Connect the VCC pin (+) of the IR Emitter module to 3.3V
- Connect the Signal pin (S) of the IR Emitter module to GPIO 8.
SCHEMATIC:
IR Emitter Module VCC → 3.3V
IR Emitter Module GND → GND
IR Module Signal → GPIO 8
CODE -- C:
const int IR_PIN = 8;
const int DOT_DURATION = 200;
const int DASH_DURATION = DOT_DURATION * 3;
const int SYMBOL_SPACE = DOT_DURATION;
const int LETTER_SPACE = DOT_DURATION * 3;
const int WORD_SPACE = DOT_DURATION * 7;
// Morse Code Look-up Table
const char* MORSE_CODE[] = {
".-", "-...", "-.-.", "-..", ".", "..-.", "--.", "....", "..", ".---", "-.-", ".-..", "--", "-.", "---", ".--.", "--.-", ".-.", "...", "-", "..-", "...-", ".--", "-..-", "-.--", "--..", // A-Z
"-----", ".----", "..---", "...--", "....-", ".....", "-....", "--...", "---..", "----." // 0-9
};
void setup() {
pinMode(IR_PIN, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Enter a message to transmit in Morse Code:");
}
void transmit(char* message) {
for (int i = 0; message[i] != '\\0'; i++) {
char c = toupper(message[i]);
const char* morse_pattern;
if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z') {
morse_pattern = MORSE_CODE[c - 'A'];
} else if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
morse_pattern = MORSE_CODE[c - '0' + 26];
} else if (c == ' ') {
delay(WORD_SPACE);
continue;
} else {
continue; // Ignore unknown characters
}
for (int j = 0; morse_pattern[j] != '\\0'; j++) {
digitalWrite(IR_PIN, HIGH); // Turn IR LED ON
if (morse_pattern[j] == '.') {
delay(DOT_DURATION);
} else { // It's a dash
delay(DASH_DURATION);
}
digitalWrite(IR_PIN, LOW); // Turn IR LED OFF
delay(SYMBOL_SPACE); // Space between dots/dashes
}
delay(LETTER_SPACE - SYMBOL_SPACE); // Space between letters
}
}
void loop() {
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
String message = Serial.readString();
message.trim();
if (message.length() > 0) {
Serial.print("Transmitting: ");
Serial.println(message);
// Convert String to char array for the function
char char_buffer[message.length() + 1];
message.toCharArray(char_buffer, message.length() + 1);
transmit(char_buffer);
Serial.println("\\nTransmission complete. Enter new message:");
}
}
}
const int DOT_DURATION = 200;
const int DASH_DURATION = DOT_DURATION * 3;
const int SYMBOL_SPACE = DOT_DURATION;
const int LETTER_SPACE = DOT_DURATION * 3;
const int WORD_SPACE = DOT_DURATION * 7;
// Morse Code Look-up Table
const char* MORSE_CODE[] = {
".-", "-...", "-.-.", "-..", ".", "..-.", "--.", "....", "..", ".---", "-.-", ".-..", "--", "-.", "---", ".--.", "--.-", ".-.", "...", "-", "..-", "...-", ".--", "-..-", "-.--", "--..", // A-Z
"-----", ".----", "..---", "...--", "....-", ".....", "-....", "--...", "---..", "----." // 0-9
};
void setup() {
pinMode(IR_PIN, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Enter a message to transmit in Morse Code:");
}
void transmit(char* message) {
for (int i = 0; message[i] != '\\0'; i++) {
char c = toupper(message[i]);
const char* morse_pattern;
if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z') {
morse_pattern = MORSE_CODE[c - 'A'];
} else if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
morse_pattern = MORSE_CODE[c - '0' + 26];
} else if (c == ' ') {
delay(WORD_SPACE);
continue;
} else {
continue; // Ignore unknown characters
}
for (int j = 0; morse_pattern[j] != '\\0'; j++) {
digitalWrite(IR_PIN, HIGH); // Turn IR LED ON
if (morse_pattern[j] == '.') {
delay(DOT_DURATION);
} else { // It's a dash
delay(DASH_DURATION);
}
digitalWrite(IR_PIN, LOW); // Turn IR LED OFF
delay(SYMBOL_SPACE); // Space between dots/dashes
}
delay(LETTER_SPACE - SYMBOL_SPACE); // Space between letters
}
}
void loop() {
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
String message = Serial.readString();
message.trim();
if (message.length() > 0) {
Serial.print("Transmitting: ");
Serial.println(message);
// Convert String to char array for the function
char char_buffer[message.length() + 1];
message.toCharArray(char_buffer, message.length() + 1);
transmit(char_buffer);
Serial.println("\\nTransmission complete. Enter new message:");
}
}
}
const int DOT_DURATION = 200; - This base unit defines the entire timing scheme. A dash is 3 dots long, the space between letters is 3 dots, etc.
const char* MORSE_CODE[] - This array is the "dictionary" that holds the dot-dash patterns for each letter and number.
transmit() - This is the main function. It loops through each character of your message, finds its pattern in the MORSE_CODE array, and then loops through that pattern to flash the IR LED for the correct dot or dash duration.
if (Serial.available() > 0) - The main loop waits for you to type a message into the Arduino IDE's Serial Monitor and press Enter.
const char* MORSE_CODE[] - This array is the "dictionary" that holds the dot-dash patterns for each letter and number.
transmit() - This is the main function. It loops through each character of your message, finds its pattern in the MORSE_CODE array, and then loops through that pattern to flash the IR LED for the correct dot or dash duration.
if (Serial.available() > 0) - The main loop waits for you to type a message into the Arduino IDE's Serial Monitor and press Enter.
CODE -- PYTHON:
from machine import Pin
from time import sleep_ms
ir_pin = Pin(8, Pin.OUT)
DOT_DURATION = 200
DASH_DURATION = DOT_DURATION * 3
SYMBOL_SPACE = DOT_DURATION
LETTER_SPACE = DOT_DURATION * 3
WORD_SPACE = DOT_DURATION * 7
# Morse Code Dictionary
MORSE_CODE_DICT = {
'A': '.-', 'B': '-...', 'C': '-.-.', 'D': '-..', 'E': '.', 'F': '..-.',
'G': '--.', 'H': '....", 'I': '..', 'J': '.---', 'K': '-.-', 'L': '.-..',
'M': '--', 'N': '-.', 'O': '---', 'P': '.--.', 'Q': '--.-', 'R': '.-.',
'S': '...', 'T': '-', 'U': '..-', 'V': '...-', 'W': '.--', 'X': '-..-',
'Y': '-.--', 'Z': '--..', '1': '.----', '2': '..---', '3': '...--',
'4': '....-', '5': '.....', '6': '-....", '7': '--...', '8': '---..',
'9': '----.', '0': '-----'
}
def transmit(message):
for char in message.upper():
if char == ' ':
sleep_ms(WORD_SPACE)
elif char in MORSE_CODE_DICT:
pattern = MORSE_CODE_DICT[char]
for symbol in pattern:
ir_pin.on()
if symbol == '.':
sleep_ms(DOT_DURATION)
else: # It's a dash
sleep_ms(DASH_DURATION)
ir_pin.off()
sleep_ms(SYMBOL_SPACE)
sleep_ms(LETTER_SPACE - SYMBOL_SPACE)
# --- Main Loop with User Input ---
print("Ready for input.")
while True:
message = input("Enter a message to transmit: ")
if len(message) > 0:
print(f"Transmitting: {message.upper()}")
transmit(message)
print("Transmission complete.")
print("-------------------------")
from time import sleep_ms
ir_pin = Pin(8, Pin.OUT)
DOT_DURATION = 200
DASH_DURATION = DOT_DURATION * 3
SYMBOL_SPACE = DOT_DURATION
LETTER_SPACE = DOT_DURATION * 3
WORD_SPACE = DOT_DURATION * 7
# Morse Code Dictionary
MORSE_CODE_DICT = {
'A': '.-', 'B': '-...', 'C': '-.-.', 'D': '-..', 'E': '.', 'F': '..-.',
'G': '--.', 'H': '....", 'I': '..', 'J': '.---', 'K': '-.-', 'L': '.-..',
'M': '--', 'N': '-.', 'O': '---', 'P': '.--.', 'Q': '--.-', 'R': '.-.',
'S': '...', 'T': '-', 'U': '..-', 'V': '...-', 'W': '.--', 'X': '-..-',
'Y': '-.--', 'Z': '--..', '1': '.----', '2': '..---', '3': '...--',
'4': '....-', '5': '.....', '6': '-....", '7': '--...', '8': '---..',
'9': '----.', '0': '-----'
}
def transmit(message):
for char in message.upper():
if char == ' ':
sleep_ms(WORD_SPACE)
elif char in MORSE_CODE_DICT:
pattern = MORSE_CODE_DICT[char]
for symbol in pattern:
ir_pin.on()
if symbol == '.':
sleep_ms(DOT_DURATION)
else: # It's a dash
sleep_ms(DASH_DURATION)
ir_pin.off()
sleep_ms(SYMBOL_SPACE)
sleep_ms(LETTER_SPACE - SYMBOL_SPACE)
# --- Main Loop with User Input ---
print("Ready for input.")
while True:
message = input("Enter a message to transmit: ")
if len(message) > 0:
print(f"Transmitting: {message.upper()}")
transmit(message)
print("Transmission complete.")
print("-------------------------")
MORSE_CODE_DICT - This dictionary is the core of the translator. It maps each character (the "key") to its dot-dash pattern (the "value").
transmit() - This function takes a message string. It loops through each character, looks up its pattern in the dictionary, and then flashes the IR LED according to the pattern.
ir_pin.on() / ir_pin.off() - These commands turn the IR LED on and off.
sleep_ms() - This function creates the precise delays needed for dots, dashes, and the spaces between letters and words, which is critical for valid Morse code.
transmit() - This function takes a message string. It loops through each character, looks up its pattern in the dictionary, and then flashes the IR LED according to the pattern.
ir_pin.on() / ir_pin.off() - These commands turn the IR LED on and off.
sleep_ms() - This function creates the precise delays needed for dots, dashes, and the spaces between letters and words, which is critical for valid Morse code.