IR Remote Controlled Robot Car
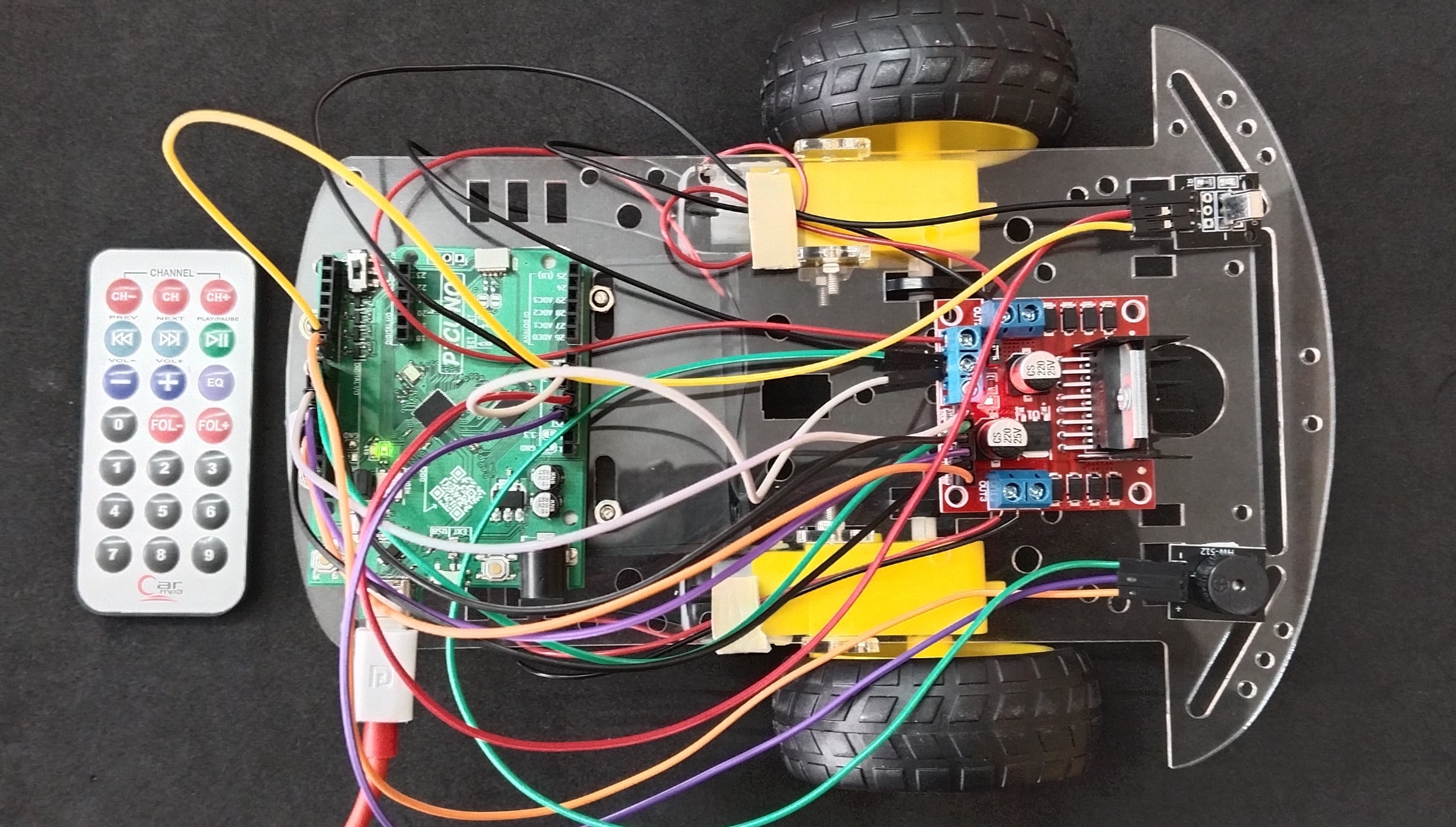
HARDWARE REQUIRED:
- PICUNO Microcontroller board
- 1 × 2-Wheel Chassis (with wheels, motors, etc.) full set
- 1 × 298N Motor Driver
- 1 × 4xAA Battery pack (with fresh or rechargeable batteries)
- 1 × HW-490 IR Receiver Module
- 1 × IR Remote Display
- 1 × Buzzer Module
- 1 × 9V Battery (optional for external power supply to PICUNO)
- Jumper wires
- USB cable
DESCRIPTION:
This project transforms the 2-wheel chassis into a fully functional remote-controlled vehicle. Using a standard IR remote, you can control the robot's movement (forward, backward, left, right), adjust its speed, and trigger special, pre-programmed maneuvers like a 360-degree spin or a horn sound. This project combines wireless communication, motor control, and state management to create a feature-rich robotic car.
LIBRARIES REQUIRED:
For C / Arduino IDE:
IRremote by shirriff, z3t0, ArminJo: The driver library for the IR receiver Module.
For Micropython / Thonny IDE:
ir_rx.py: The custom library file for the IR receiver module, saved to the PICUNO board.
ASSEMBLY OF 2-WHEEL CHASIS KIT:
1.) Prepare the Chassis: If your chassis parts are acrylic, they often come with a protective paper or plastic film. Peel this film off all the pieces.
2.) Mount the Motors: Attach the two yellow DC motors to the main chassis plate. Use the brackets and long screws/nuts that came with the kit to secure them firmly in place.
3.) Attach the Wheels: Push the two main wheels onto the plastic shafts of the motors. They should be a snug fit.
4.) Attach the Caster Wheel: Mount the third, free-spinning wheel (the caster or ball wheel) to the other end of the chassis. This wheel acts as the front or back support and allows the robot to turn easily.
5.) Mount the Battery Holder: Use screws to attach the 4xAA battery pack at the bottom of the chassis.
6.) Mount the Electronics: Finally, mount the PICUNO, L298N motor driver, IR Receiver and Buzzer onto the chassis, usually using screws/double tape. Position them such that to easily run wires to the motors.
LIBRARIES REQUIRED:
For C / Arduino IDE:
IRremote by shirriff, z3t0, ArminJo: The driver library for the IR receiver Module.
For Micropython / Thonny IDE:
ir_rx.py: The custom library file for the IR receiver module, saved to the PICUNO board.
ASSEMBLY OF 2-WHEEL CHASIS KIT:
1.) Prepare the Chassis: If your chassis parts are acrylic, they often come with a protective paper or plastic film. Peel this film off all the pieces.
2.) Mount the Motors: Attach the two yellow DC motors to the main chassis plate. Use the brackets and long screws/nuts that came with the kit to secure them firmly in place.
3.) Attach the Wheels: Push the two main wheels onto the plastic shafts of the motors. They should be a snug fit.
4.) Attach the Caster Wheel: Mount the third, free-spinning wheel (the caster or ball wheel) to the other end of the chassis. This wheel acts as the front or back support and allows the robot to turn easily.
5.) Mount the Battery Holder: Use screws to attach the 4xAA battery pack at the bottom of the chassis.
6.) Mount the Electronics: Finally, mount the PICUNO, L298N motor driver, IR Receiver and Buzzer onto the chassis, usually using screws/double tape. Position them such that to easily run wires to the motors.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:

- OUT1 & OUT2: Connect these two screw terminals to the outputs for the first motor (e.g., the left wheel). Connect the two wires from one DC motor here.
- OUT3 & OUT4: Connect these two screw terminals to the outputs for the second motor (e.g., the right wheel). Connect the two wires from the other DC motor here.
- Connect the positive terminal (+) of the 4xAA battery pack to the 12V screw terminal.
- Connect the negative terminal (-) of the 4xAA battery pack to the GND screw terminal.
- Also connect the GND terminal on the L298N to a GND pin on the microcontroller to create a common ground.
- Connect the IN1 pin (Left motor) to GPIO 8.
- Connect the IN2 pin (Left motor) to GPIO 9.
- Connect the ENA pin (Left motor speed) to GPIO 10.
- Connect the IN1 pin (Right motor) to GPIO 11.
- Connect the IN2 pin (Right motor) to GPIO 12.
- Connect the ENB pin (Right motor speed) to GPIO 13.
NOTE: Remove the ENA and ENB jumpers on the L298N motor driver.
- Connect the GND (-) pin to GND pin.
- Connect the VCC (+) pin to 5V.
- Connect the Signal (S) pin to GPIO 6.
- Connect the GND (-) pin to GND pin.
- Connect the VCC (+) pin to 5V.
- Connect the Signal (S) pin to GPIO 7.
OPTIONAL: You can power the PICUNO using an external power supply (9V Battery) through DC Jack, once you have uploaded the code to the microcontroller.
SCHEMATIC:
L298N Motor Driver:
OUT2 & OUT2 → Outputs for the Left Motor.
OUT3 & OUT4 → Outputs for the Right Motor.
12V → positive terminal (+) of 4xAA battery pack.
GND → negative terminal (-) of 4xAA battery pack → GND on PICUNO.
IN1 (Left Motor) → GPIO 8
IN2 (Left Motor) → GPIO 9
ENA (Left Motor speed) → GPIO 10
IN3 (Right Motor) → GPIO 11
IN4 (Right Motor) → GPIO 12
ENB (Right Motor) → GPIO 13
IR Receiver Module:
VCC / (+) → 5V
GND / (-) → GND
Signal (S) → GPIO 6
Buzzer Module:
VCC / (+) → 3.3V
GND / (-) → GND
Signal (S) → GPIO 7
CODE -- C:
#include <IRremote.hpp>
const int L_IN1=8, L_IN2=9, L_ENA=10;
const int R_IN3=11, R_IN4=12, R_ENB=13;
const int IR_PIN = 6;
const int BUZZER_PIN = 7;
// --- Global State Variables ---
String current_command = "stop";
int current_speed = 80;
// --- Helper Functions ---
void setMotorSpeed(char motor, int speed) {
int duty = map(abs(speed), 0, 100, 0, 255);
if (motor == 'L') {
if (speed > 0) { digitalWrite(L_IN1, HIGH); digitalWrite(L_IN2, LOW); }
else if (speed < 0) { digitalWrite(L_IN1, LOW); digitalWrite(L_IN2, HIGH); }
else { digitalWrite(L_IN1, LOW); digitalWrite(L_IN2, LOW); }
analogWrite(L_ENA, duty);
} else if (motor == 'R') {
if (speed > 0) { digitalWrite(R_IN3, HIGH); digitalWrite(R_IN4, LOW); }
else if (speed < 0) { digitalWrite(R_IN3, LOW); digitalWrite(R_IN4, HIGH); }
else { digitalWrite(R_IN3, LOW); digitalWrite(R_IN4, LOW); }
analogWrite(R_ENB, duty);
}
}
void forward() { setMotorSpeed('L', current_speed); setMotorSpeed('R', current_speed); }
void backward() { setMotorSpeed('L', -current_speed); setMotorSpeed('R', -current_speed); }
void turn_left() { setMotorSpeed('L', -current_speed); setMotorSpeed('R', current_speed); }
void turn_right() { setMotorSpeed('L', current_speed); setMotorSpeed('R', -current_speed); }
void stopMotors() { setMotorSpeed('L', 0); setMotorSpeed('R', 0); }
void spin_left() {
Serial.println("Executing: Spin Left");
setMotorSpeed('L', -80); setMotorSpeed('R', 80);
delay(1600);
stopMotors();
}
void spin_right() {
Serial.println("Executing: Spin Right");
setMotorSpeed('L', 80); setMotorSpeed('R', -80);
delay(1600);
stopMotors();
}
void play_tune() {
Serial.println("Executing: Horn Sound");
tone(BUZZER_PIN, 3000, 1000);
}
void setup() {
pinMode(L_IN1, OUTPUT); pinMode(L_IN2, OUTPUT); pinMode(L_ENA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(R_IN3, OUTPUT); pinMode(R_IN4, OUTPUT); pinMode(R_ENB, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BUZZER_PIN, OUTPUT);
IrReceiver.begin(IR_PIN, ENABLE_LED_FEEDBACK);
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("IR Robot Ready. Use your remote to control.");
stopMotors();
}
void loop() {
if (IrReceiver.decode()) {
if (IrReceiver.decodedIRData.decodedRawData != 0) {
unsigned long code = IrReceiver.decodedIRData.decodedRawData;
Serial.print("Code Received: 0x");
Serial.println(code, HEX);
if (code == 0xF807FF00) { current_command = "forward"; Serial.println("Command: Moving forward"); }
else if (code == 0xEA15FF00) { current_command = "backward"; Serial.println("Command: Moving backward"); }
else if (code == 0xBA45FF00) { current_command = "left"; Serial.println("Command: Turning left"); }
else if (code == 0xB847FF00) { current_command = "right"; Serial.println("Command: Turning right"); }
else if (code == 0xBC43FF00) { current_command = "stop"; Serial.println("Command: stop"); }
else if (code == 0xE31CFF00) { current_speed = 50; Serial.println("Speed set to: 50%"); }
else if (code == 0xA55AFF00) { current_speed = 60; Serial.println("Speed set to: 60%"); }
else if (code == 0xBD42FF00) { current_speed = 70; Serial.println("Speed set to: 70%"); }
else if (code == 0xAD52FF00) { current_speed = 80; Serial.println("Speed set to: 80%"); }
else if (code == 0xB54AFF00) { current_speed = 90; Serial.println("Speed set to: 90%"); }
else if (code == 0xE916FF00) { current_speed = 100; Serial.println("Speed set to: 100%"); }
else if (code == 0xBB44FF00) { current_command = "spin_left"; }
else if (code == 0xBF40FF00) { current_command = "spin_right"; }
else if (code == 0xF609FF00) { current_command = "play_tune"; }
}
IrReceiver.resume();
}
// Act on the current command
if (current_command == "forward") { forward(); }
else if (current_command == "backward") { backward(); }
else if (current_command == "left") { turn_left(); }
else if (current_command == "right") { turn_right(); }
else if (current_command == "stop") { stopMotors(); }
else if (current_command == "spin_left") { spin_left(); current_command = "stop"; }
else if (current_command == "spin_right") { spin_right(); current_command = "stop"; }
else if (current_command == "play_tune") { play_tune(); current_command = "stop"; }
delay(50);
}
const int L_IN1=8, L_IN2=9, L_ENA=10;
const int R_IN3=11, R_IN4=12, R_ENB=13;
const int IR_PIN = 6;
const int BUZZER_PIN = 7;
// --- Global State Variables ---
String current_command = "stop";
int current_speed = 80;
// --- Helper Functions ---
void setMotorSpeed(char motor, int speed) {
int duty = map(abs(speed), 0, 100, 0, 255);
if (motor == 'L') {
if (speed > 0) { digitalWrite(L_IN1, HIGH); digitalWrite(L_IN2, LOW); }
else if (speed < 0) { digitalWrite(L_IN1, LOW); digitalWrite(L_IN2, HIGH); }
else { digitalWrite(L_IN1, LOW); digitalWrite(L_IN2, LOW); }
analogWrite(L_ENA, duty);
} else if (motor == 'R') {
if (speed > 0) { digitalWrite(R_IN3, HIGH); digitalWrite(R_IN4, LOW); }
else if (speed < 0) { digitalWrite(R_IN3, LOW); digitalWrite(R_IN4, HIGH); }
else { digitalWrite(R_IN3, LOW); digitalWrite(R_IN4, LOW); }
analogWrite(R_ENB, duty);
}
}
void forward() { setMotorSpeed('L', current_speed); setMotorSpeed('R', current_speed); }
void backward() { setMotorSpeed('L', -current_speed); setMotorSpeed('R', -current_speed); }
void turn_left() { setMotorSpeed('L', -current_speed); setMotorSpeed('R', current_speed); }
void turn_right() { setMotorSpeed('L', current_speed); setMotorSpeed('R', -current_speed); }
void stopMotors() { setMotorSpeed('L', 0); setMotorSpeed('R', 0); }
void spin_left() {
Serial.println("Executing: Spin Left");
setMotorSpeed('L', -80); setMotorSpeed('R', 80);
delay(1600);
stopMotors();
}
void spin_right() {
Serial.println("Executing: Spin Right");
setMotorSpeed('L', 80); setMotorSpeed('R', -80);
delay(1600);
stopMotors();
}
void play_tune() {
Serial.println("Executing: Horn Sound");
tone(BUZZER_PIN, 3000, 1000);
}
void setup() {
pinMode(L_IN1, OUTPUT); pinMode(L_IN2, OUTPUT); pinMode(L_ENA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(R_IN3, OUTPUT); pinMode(R_IN4, OUTPUT); pinMode(R_ENB, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BUZZER_PIN, OUTPUT);
IrReceiver.begin(IR_PIN, ENABLE_LED_FEEDBACK);
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("IR Robot Ready. Use your remote to control.");
stopMotors();
}
void loop() {
if (IrReceiver.decode()) {
if (IrReceiver.decodedIRData.decodedRawData != 0) {
unsigned long code = IrReceiver.decodedIRData.decodedRawData;
Serial.print("Code Received: 0x");
Serial.println(code, HEX);
if (code == 0xF807FF00) { current_command = "forward"; Serial.println("Command: Moving forward"); }
else if (code == 0xEA15FF00) { current_command = "backward"; Serial.println("Command: Moving backward"); }
else if (code == 0xBA45FF00) { current_command = "left"; Serial.println("Command: Turning left"); }
else if (code == 0xB847FF00) { current_command = "right"; Serial.println("Command: Turning right"); }
else if (code == 0xBC43FF00) { current_command = "stop"; Serial.println("Command: stop"); }
else if (code == 0xE31CFF00) { current_speed = 50; Serial.println("Speed set to: 50%"); }
else if (code == 0xA55AFF00) { current_speed = 60; Serial.println("Speed set to: 60%"); }
else if (code == 0xBD42FF00) { current_speed = 70; Serial.println("Speed set to: 70%"); }
else if (code == 0xAD52FF00) { current_speed = 80; Serial.println("Speed set to: 80%"); }
else if (code == 0xB54AFF00) { current_speed = 90; Serial.println("Speed set to: 90%"); }
else if (code == 0xE916FF00) { current_speed = 100; Serial.println("Speed set to: 100%"); }
else if (code == 0xBB44FF00) { current_command = "spin_left"; }
else if (code == 0xBF40FF00) { current_command = "spin_right"; }
else if (code == 0xF609FF00) { current_command = "play_tune"; }
}
IrReceiver.resume();
}
// Act on the current command
if (current_command == "forward") { forward(); }
else if (current_command == "backward") { backward(); }
else if (current_command == "left") { turn_left(); }
else if (current_command == "right") { turn_right(); }
else if (current_command == "stop") { stopMotors(); }
else if (current_command == "spin_left") { spin_left(); current_command = "stop"; }
else if (current_command == "spin_right") { spin_right(); current_command = "stop"; }
else if (current_command == "play_tune") { play_tune(); current_command = "stop"; }
delay(50);
}
if/else if chain - if/else if structure is used to check the received IR code against your list of known button codes.
current_command String - This variable stores the last valid command received. The loop() function continuously checks this variable to maintain the robot's action (e.g., keep moving forward).
analogWrite() - sending a PWM signal to the L298N's enable pins to control motor speed. The map() function is used to convert the 0-100 speed percentage to the required 0-255 range.
Special Moves: When a special move command is received, the code calls the corresponding function (which contains its own delay()) and then resets the current_command to "stop" to wait for the next user input.
current_command String - This variable stores the last valid command received. The loop() function continuously checks this variable to maintain the robot's action (e.g., keep moving forward).
analogWrite() - sending a PWM signal to the L298N's enable pins to control motor speed. The map() function is used to convert the 0-100 speed percentage to the required 0-255 range.
Special Moves: When a special move command is received, the code calls the corresponding function (which contains its own delay()) and then resets the current_command to "stop" to wait for the next user input.
CODE -- PYTHON:
from machine import Pin, PWM
from time import sleep_ms
from ir_rx import IR_RX
L_IN1 = Pin(8, Pin.OUT); L_IN2 = Pin(9, Pin.OUT); L_ENA = PWM(Pin(10))
R_IN3 = Pin(11, Pin.OUT); R_IN4 = Pin(12, Pin.OUT); R_ENB = PWM(Pin(13))
L_ENA.freq(1000); R_ENB.freq(1000)
IR_PIN = 6
BUZZER_PIN = 7
buzzer = PWM(Pin(BUZZER_PIN))
# --- Global State Variables ---
current_command = 'stop'
current_speed = 80
REMOTE_CODES = {
0x2b: 'forward', # VOL+ button
0xf: 'backward', # VOL- button
0x8b: 'left', # CH- button
0x8d: 'right', # CH+ button
0x87: 'stop', # PLAY/PAUSE button
0x39: 50, 0xb5: 60, 0x85: 70, 0xa5: 80, 0x95: 90, # 5-9 buttons for setting up speed
0x2d: 100, # button 0 for 100% speed
0x89: 'spin_left', # PREV button
0x81: 'spin_right', # NEXT button
0x13: 'play_tune' # EQ button
}
# --- IR Callback Function---
def ir_callback(data, addr, ctrl):
global current_command, current_speed
if data > 0:
print(f"Code Received: {hex(data)}")
if data in REMOTE_CODES:
action = REMOTE_CODES[data]
if isinstance(action, str):
current_command = action
print(f"Command: {current_command}")
elif isinstance(action, int):
current_speed = action
print(f"Speed set to: {current_speed}%")
# --- Motor Control Functions ---
def set_motor_speed(motor, speed):
duty = int(abs(speed) / 100 * 65535)
if motor == 'left':
if speed > 0: L_IN1.high(); L_IN2.low()
elif speed < 0: L_IN1.low(); L_IN2.high()
else: L_IN1.low(); L_IN2.low()
L_ENA.duty_u16(duty)
elif motor == 'right':
if speed > 0: R_IN3.high(); R_IN4.low()
elif speed < 0: R_IN3.low(); R_IN4.high()
else: R_IN3.low(); R_IN4.high()
R_ENB.duty_u16(duty)
def forward(): set_motor_speed('left', current_speed); set_motor_speed('right', current_speed)
def backward(): set_motor_speed('left', -current_speed); set_motor_speed('right', -current_speed)
def turn_left(): set_motor_speed('left', -current_speed); set_motor_speed('right', current_speed)
def turn_right(): set_motor_speed('left', current_speed); set_motor_speed('right', -current_speed)
def stop(): set_motor_speed('left', 0); set_motor_speed('right', 0)
def spin_left():
print("Executing: Spin Left")
set_motor_speed('left', -80)
set_motor_speed('right', 80)
sleep_ms(3600) # Adjust this time for a perfect 360 spin
stop()
def spin_right():
print("Executing: Spin Right")
set_motor_speed('left', 80)
set_motor_speed('right', -80)
sleep_ms(3600) # Adjust this time for a perfect 360 spin
stop()
def play_tune():
print("Executing: Horn Sound")
HORN_FREQUENCY = 3000 # in Hz
HORN_DURATION_MS = 1000
buzzer.freq(HORN_FREQUENCY)
buzzer.duty_u16(32768) # Turn sound on (50% volume)
sleep_ms(HORN_DURATION_MS)
buzzer.duty_u16(0)
# --- Main Program ---
receiver = IR_RX(Pin(IR_PIN, Pin.IN), ir_callback)
print("IR Robot Ready. Use your remote to control.")
stop()
while True:
# --- Check for continuous driving commands ---
if current_command == 'forward':
forward()
elif current_command == 'backward':
backward()
elif current_command == 'left':
turn_left()
elif current_command == 'right':
turn_right()
elif current_command == 'stop':
stop()
elif current_command == 'spin_left':
spin_left()
current_command = 'stop' # Reset to stop after the move is done
elif current_command == 'spin_right':
spin_right()
current_command = 'stop'
elif current_command == 'play_tune':
play_tune()
current_command = 'stop'
sleep_ms(50)
from time import sleep_ms
from ir_rx import IR_RX
L_IN1 = Pin(8, Pin.OUT); L_IN2 = Pin(9, Pin.OUT); L_ENA = PWM(Pin(10))
R_IN3 = Pin(11, Pin.OUT); R_IN4 = Pin(12, Pin.OUT); R_ENB = PWM(Pin(13))
L_ENA.freq(1000); R_ENB.freq(1000)
IR_PIN = 6
BUZZER_PIN = 7
buzzer = PWM(Pin(BUZZER_PIN))
# --- Global State Variables ---
current_command = 'stop'
current_speed = 80
REMOTE_CODES = {
0x2b: 'forward', # VOL+ button
0xf: 'backward', # VOL- button
0x8b: 'left', # CH- button
0x8d: 'right', # CH+ button
0x87: 'stop', # PLAY/PAUSE button
0x39: 50, 0xb5: 60, 0x85: 70, 0xa5: 80, 0x95: 90, # 5-9 buttons for setting up speed
0x2d: 100, # button 0 for 100% speed
0x89: 'spin_left', # PREV button
0x81: 'spin_right', # NEXT button
0x13: 'play_tune' # EQ button
}
# --- IR Callback Function---
def ir_callback(data, addr, ctrl):
global current_command, current_speed
if data > 0:
print(f"Code Received: {hex(data)}")
if data in REMOTE_CODES:
action = REMOTE_CODES[data]
if isinstance(action, str):
current_command = action
print(f"Command: {current_command}")
elif isinstance(action, int):
current_speed = action
print(f"Speed set to: {current_speed}%")
# --- Motor Control Functions ---
def set_motor_speed(motor, speed):
duty = int(abs(speed) / 100 * 65535)
if motor == 'left':
if speed > 0: L_IN1.high(); L_IN2.low()
elif speed < 0: L_IN1.low(); L_IN2.high()
else: L_IN1.low(); L_IN2.low()
L_ENA.duty_u16(duty)
elif motor == 'right':
if speed > 0: R_IN3.high(); R_IN4.low()
elif speed < 0: R_IN3.low(); R_IN4.high()
else: R_IN3.low(); R_IN4.high()
R_ENB.duty_u16(duty)
def forward(): set_motor_speed('left', current_speed); set_motor_speed('right', current_speed)
def backward(): set_motor_speed('left', -current_speed); set_motor_speed('right', -current_speed)
def turn_left(): set_motor_speed('left', -current_speed); set_motor_speed('right', current_speed)
def turn_right(): set_motor_speed('left', current_speed); set_motor_speed('right', -current_speed)
def stop(): set_motor_speed('left', 0); set_motor_speed('right', 0)
def spin_left():
print("Executing: Spin Left")
set_motor_speed('left', -80)
set_motor_speed('right', 80)
sleep_ms(3600) # Adjust this time for a perfect 360 spin
stop()
def spin_right():
print("Executing: Spin Right")
set_motor_speed('left', 80)
set_motor_speed('right', -80)
sleep_ms(3600) # Adjust this time for a perfect 360 spin
stop()
def play_tune():
print("Executing: Horn Sound")
HORN_FREQUENCY = 3000 # in Hz
HORN_DURATION_MS = 1000
buzzer.freq(HORN_FREQUENCY)
buzzer.duty_u16(32768) # Turn sound on (50% volume)
sleep_ms(HORN_DURATION_MS)
buzzer.duty_u16(0)
# --- Main Program ---
receiver = IR_RX(Pin(IR_PIN, Pin.IN), ir_callback)
print("IR Robot Ready. Use your remote to control.")
stop()
while True:
# --- Check for continuous driving commands ---
if current_command == 'forward':
forward()
elif current_command == 'backward':
backward()
elif current_command == 'left':
turn_left()
elif current_command == 'right':
turn_right()
elif current_command == 'stop':
stop()
elif current_command == 'spin_left':
spin_left()
current_command = 'stop' # Reset to stop after the move is done
elif current_command == 'spin_right':
spin_right()
current_command = 'stop'
elif current_command == 'play_tune':
play_tune()
current_command = 'stop'
sleep_ms(50)
ir_callback() function - This is an interrupt-driven function that runs automatically whenever an IR code is received. It checks the code against the REMOTE_CODES dictionary and updates the global current_command or current_speed variables.
REMOTE_CODES dictionary - This is the heart of the control system. It maps the unique hexadecimal codes from your specific remote to a command string (like 'forward') or a speed value (like 50).
current_command variable - This global variable acts as the robot's "brain" or memory. The main while loop continuously checks this variable to know what action it should be performing.
Special Moves Logic: When a special move like 'spin_left' is triggered, the code executes the action and then immediately resets current_command to 'stop' so the robot waits for a new command.
REMOTE_CODES dictionary - This is the heart of the control system. It maps the unique hexadecimal codes from your specific remote to a command string (like 'forward') or a speed value (like 50).
current_command variable - This global variable acts as the robot's "brain" or memory. The main while loop continuously checks this variable to know what action it should be performing.
Special Moves Logic: When a special move like 'spin_left' is triggered, the code executes the action and then immediately resets current_command to 'stop' so the robot waits for a new command.