Secret Tap Detector
HARDWARE REQUIRED:
- PICUNO Microcontroller board
- 1 × HW-480 Two-colour LED Module
- 1 × SG90 Servo Motor
- 1 × HW-494 Touch sensor Module
- 1 × 4xAA Battery Pack (For external supply)
- Jumper wires
- USB cable
DESCRIPTION:
This project creates a lock that opens not with a key, but with a secret rhythm. The user must tap a specific pattern on the touch sensor (e.g., two quick taps, a pause, then another two quick taps). The program measures the time intervals between the taps and compares them to a pre-defined secret pattern. If the rhythm is correct, a servo unlocks and a green LED flashes. If the rhythm is wrong or too slow, a red LED indicates failure.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
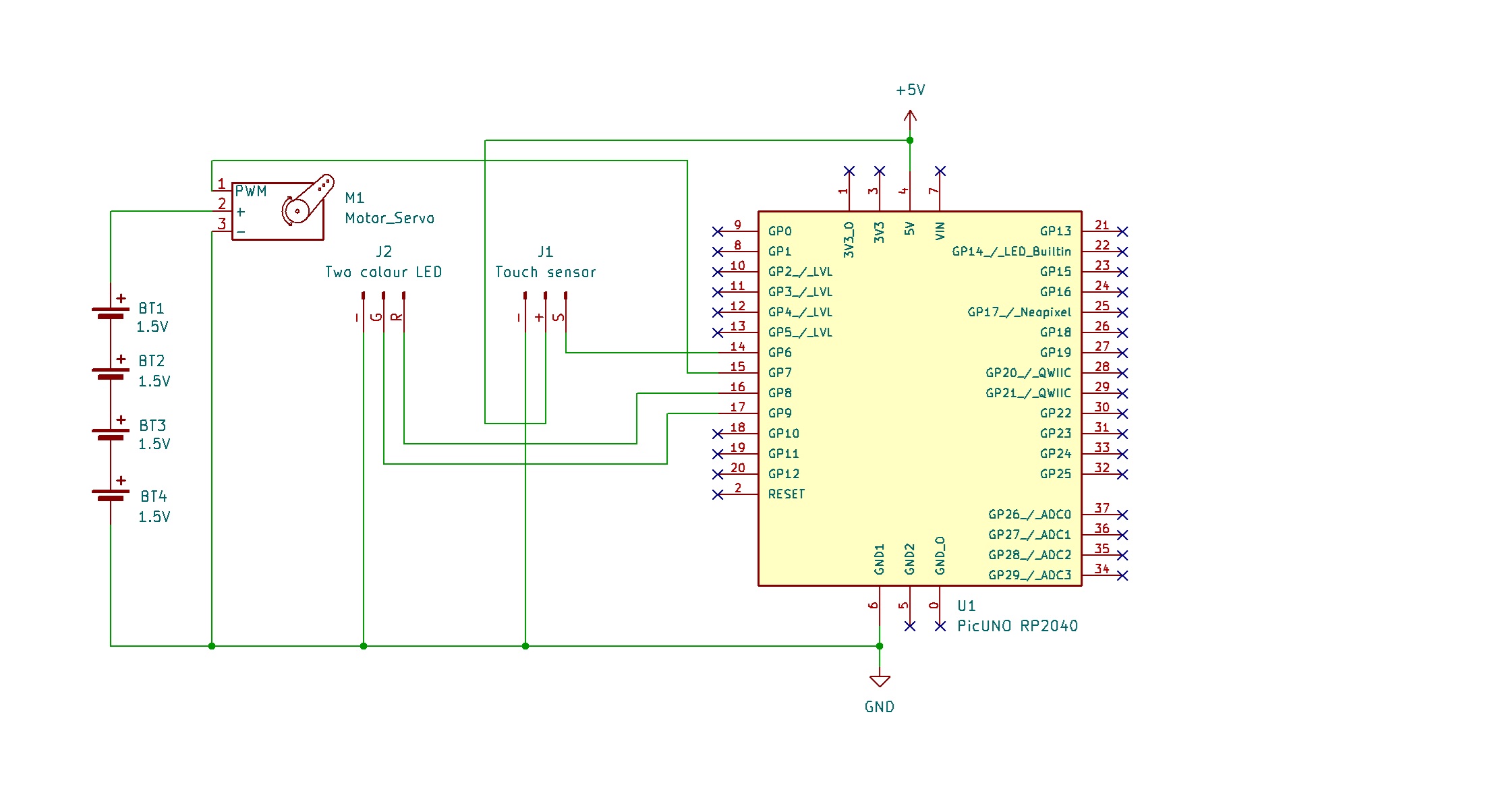
- Connect the Servo's VCC (Red) pin to the Positive (+) terminal of the 4xAA Battery Pack.
- Connect the Servo's GND (Brown) pin to GND.
- Connect the Servo's Signal (Yellow) pin to GPIO 7.
- Connect the negative terminal of the 4xAA Battery Pack to Common GND on breadboard.
- Connect the Green (G) pin to GPIO 9.
- Connect the Red (R) pin to GPIO 8.
- Connect the GND (-) pin to GND.
- Connect the GND (-) pin to GND pin.
- Connect the VCC (+) pin to 3.3V.
- Connect the Digital Output (DO) pin to GPIO 6.
SCHEMATIC:
Servo Motor:
VCC (Red Wire) → 4xAA Battery Pack (+)
GND (Brown Wire) → GND
Signal (Yellow Wire) → GPIO 7
Two-colour LED Module:
Green LED (G) → GPIO 9
Red LED (R) → GPIO 8
GND (-) → GND
Touch Sensor Module:
VCC / (+) → 5V
GND / (-) → GND
Digital Output (DO) → GPIO 6
Common Ground Connection:
4xAA Battery Pack (-) → PICUNO Board GND
CODE -- C:
#include <Servo.h>
const int SENSOR_PIN = 6;
const int GREEN_LED_PIN = 9;
const int RED_LED_PIN = 8;
const int SERVO_PIN = 7;
Servo myServo;
// --- Secret Tap Pattern ---
// 1 = short delay, 2 = long delay. This is for tap, (short), tap, (long), tap
const int secretPattern[] = {1, 2, 1};
const int patternLength = 3;
// --- Timing Thresholds (in milliseconds) ---
const int shortDelayMax = 400;
const int longDelayMin = 500;
const int longDelayMax = 1500;
const long sequenceTimeout = 3000;
// --- State Variables ---
int tapCount = 0;
unsigned long lastTapTime = 0;
bool tapState = false;
bool lastTapState = false;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(SENSOR_PIN, INPUT);
pinMode(GREEN_LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RED_LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
myServo.attach(SERVO_PIN, 500, 2500);
resetSequence();
}
void loop() {
lastTapState = tapState;
tapState = digitalRead(SENSOR_PIN);
if (tapState == HIGH && lastTapState == LOW) {
unsigned long currentTime = millis();
if (tapCount == 0) {
startSequence();
} else {
long interval = currentTime - lastTapTime;
int tapType = 0;
if (interval < shortDelayMax) tapType = 1; // Short
else if (interval > longDelayMin && interval < longDelayMax) tapType = 2;
if (tapType == secretPattern[tapCount - 1]) {
Serial.print("Correct tap "); Serial.println(tapCount);
lastTapTime = currentTime;
tapCount++;
} else {
failSequence();
}
}
}
if (tapCount == patternLength) {
successSequence();
}
if (tapCount > 0 && millis() - lastTapTime > sequenceTimeout) {
Serial.println("Sequence timed out.");
failSequence();
}
}
void startSequence() {
Serial.println("Sequence started...");
lastTapTime = millis();
tapCount = 1;
}
void successSequence() {
Serial.println("ACCESS GRANTED!");
digitalWrite(GREEN_LED_PIN, LOW); // Turn off green
for (int i=0; i<5; i++) {
digitalWrite(GREEN_LED_PIN, HIGH); delay(100);
digitalWrite(GREEN_LED_PIN, LOW); delay(100);
}
myServo.write(90); // Unlock
delay(5000);
resetSequence();
}
void failSequence() {
Serial.println("ACCESS DENIED!");
digitalWrite(GREEN_LED_PIN, LOW); // Turn off green
for (int i=0; i<3; i++) {
digitalWrite(RED_LED_PIN, HIGH); delay(250);
digitalWrite(RED_LED_PIN, LOW); delay(250);
}
resetSequence();
}
void resetSequence() {
myServo.write(1);
tapCount = 0;
digitalWrite(RED_LED_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(GREEN_LED_PIN, HIGH);
Serial.println("Ready for new sequence.");
}
const int SENSOR_PIN = 6;
const int GREEN_LED_PIN = 9;
const int RED_LED_PIN = 8;
const int SERVO_PIN = 7;
Servo myServo;
// --- Secret Tap Pattern ---
// 1 = short delay, 2 = long delay. This is for tap, (short), tap, (long), tap
const int secretPattern[] = {1, 2, 1};
const int patternLength = 3;
// --- Timing Thresholds (in milliseconds) ---
const int shortDelayMax = 400;
const int longDelayMin = 500;
const int longDelayMax = 1500;
const long sequenceTimeout = 3000;
// --- State Variables ---
int tapCount = 0;
unsigned long lastTapTime = 0;
bool tapState = false;
bool lastTapState = false;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(SENSOR_PIN, INPUT);
pinMode(GREEN_LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RED_LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
myServo.attach(SERVO_PIN, 500, 2500);
resetSequence();
}
void loop() {
lastTapState = tapState;
tapState = digitalRead(SENSOR_PIN);
if (tapState == HIGH && lastTapState == LOW) {
unsigned long currentTime = millis();
if (tapCount == 0) {
startSequence();
} else {
long interval = currentTime - lastTapTime;
int tapType = 0;
if (interval < shortDelayMax) tapType = 1; // Short
else if (interval > longDelayMin && interval < longDelayMax) tapType = 2;
if (tapType == secretPattern[tapCount - 1]) {
Serial.print("Correct tap "); Serial.println(tapCount);
lastTapTime = currentTime;
tapCount++;
} else {
failSequence();
}
}
}
if (tapCount == patternLength) {
successSequence();
}
if (tapCount > 0 && millis() - lastTapTime > sequenceTimeout) {
Serial.println("Sequence timed out.");
failSequence();
}
}
void startSequence() {
Serial.println("Sequence started...");
lastTapTime = millis();
tapCount = 1;
}
void successSequence() {
Serial.println("ACCESS GRANTED!");
digitalWrite(GREEN_LED_PIN, LOW); // Turn off green
for (int i=0; i<5; i++) {
digitalWrite(GREEN_LED_PIN, HIGH); delay(100);
digitalWrite(GREEN_LED_PIN, LOW); delay(100);
}
myServo.write(90); // Unlock
delay(5000);
resetSequence();
}
void failSequence() {
Serial.println("ACCESS DENIED!");
digitalWrite(GREEN_LED_PIN, LOW); // Turn off green
for (int i=0; i<3; i++) {
digitalWrite(RED_LED_PIN, HIGH); delay(250);
digitalWrite(RED_LED_PIN, LOW); delay(250);
}
resetSequence();
}
void resetSequence() {
myServo.write(1);
tapCount = 0;
digitalWrite(RED_LED_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(GREEN_LED_PIN, HIGH);
Serial.println("Ready for new sequence.");
}
secretPattern array - This array stores your secret rhythm. 1 represents a short pause and 2 represents a long pause between taps.
Rising Edge Detection - The logic if (tapState == HIGH && lastTapState == LOW) detects the exact moment a new tap begins, preventing one long touch from being counted multiple times.
millis() - This function gets the current time from the Arduino's internal clock. It's used to measure the precise time interval between each tap to check if the rhythm is correct.
Timing Thresholds - Variables like shortDelayMax define what the code considers a "short" or "long" pause, allowing you to calibrate the required rhythm.
tapCount variable - This acts as the program's memory, keeping track of how many correct taps have been entered in the current sequence.
Helper Functions - The code is organized into functions like successSequence() and failSequence() to keep the main loop clean and make the different outcomes easy to manage.
Rising Edge Detection - The logic if (tapState == HIGH && lastTapState == LOW) detects the exact moment a new tap begins, preventing one long touch from being counted multiple times.
millis() - This function gets the current time from the Arduino's internal clock. It's used to measure the precise time interval between each tap to check if the rhythm is correct.
Timing Thresholds - Variables like shortDelayMax define what the code considers a "short" or "long" pause, allowing you to calibrate the required rhythm.
tapCount variable - This acts as the program's memory, keeping track of how many correct taps have been entered in the current sequence.
Helper Functions - The code is organized into functions like successSequence() and failSequence() to keep the main loop clean and make the different outcomes easy to manage.
CODE -- PYTHON:
from machine import Pin, PWM
from time import sleep_ms, ticks_ms, ticks_diff
SENSOR_PIN = 6
GREEN_LED_PIN = 9
RED_LED_PIN = 8
SERVO_PIN = 7
# --- Component Objects ---
touch_sensor = Pin(SENSOR_PIN, Pin.IN)
green_led = Pin(GREEN_LED_PIN, Pin.OUT)
red_led = Pin(RED_LED_PIN, Pin.OUT)
servo_pwm = PWM(Pin(SERVO_PIN))
servo_pwm.freq(50)
# --- Secret Tap Pattern ---
# 1 = short delay, 2 = long delay. This is for tap, (short), tap, (long), tap
secret_pattern = [1, 2]
pattern_length = 3 # Total number of taps required
# --- Timing Thresholds (in milliseconds) ---
SHORT_DELAY_MAX = 400
LONG_DELAY_MIN = 500
LONG_DELAY_MAX = 1500
SEQUENCE_TIMEOUT = 3000
# --- State Variables ---
tap_count = 0
last_tap_time = 0
last_sensor_state = 0
# --- Helper Functions ---
def set_servo_angle(angle):
duty = ((angle / 180) * (8350 - 1350)) + 1350
servo_pwm.duty_u16(int(duty))
def reset_sequence():
global tap_count
set_servo_angle(1) # Lock
red_led.low()
green_led.high() # Ready state
tap_count = 0
print("Ready for new sequence.")
def success_sequence():
print("ACCESS GRANTED!")
green_led.low()
for i in range(5):
green_led.high(); sleep_ms(100)
green_led.low(); sleep_ms(100)
set_servo_angle(90) # Unlock
sleep_ms(5000)
reset_sequence()
def fail_sequence():
print("ACCESS DENIED!")
green_led.low()
for i in range(3):
red_led.high(); sleep_ms(250)
red_led.low(); sleep_ms(250)
reset_sequence()
# --- Initial State ---
reset_sequence()
# --- Main Loop ---
while True:
current_sensor_state = touch_sensor.value()
# Check for a new tap (a rising edge from 0 to 1)
if current_sensor_state == 1 and last_sensor_state == 0:
current_time = ticks_ms()
if tap_count == 0: # First tap
print("Sequence started...")
last_tap_time = current_time
tap_count = 1
else: # Subsequent taps
interval = ticks_diff(current_time, last_tap_time)
tap_type = 0
if interval < SHORT_DELAY_MAX: tap_type = 1 # Short
elif interval > LONG_DELAY_MIN and interval < LONG_DELAY_MAX: tap_type = 2 # Long
if tap_type == secret_pattern[tap_count - 1]:
print(f"Correct tap {tap_count}")
last_tap_time = current_time
tap_count += 1
else:
fail_sequence()
# Check for success
if tap_count == pattern_length:
success_sequence()
# Check for timeout
if tap_count > 0 and ticks_diff(ticks_ms(), last_tap_time) > SEQUENCE_TIMEOUT:
print("Sequence timed out.")
fail_sequence()
last_sensor_state = current_sensor_state
sleep_ms(20)
from time import sleep_ms, ticks_ms, ticks_diff
SENSOR_PIN = 6
GREEN_LED_PIN = 9
RED_LED_PIN = 8
SERVO_PIN = 7
# --- Component Objects ---
touch_sensor = Pin(SENSOR_PIN, Pin.IN)
green_led = Pin(GREEN_LED_PIN, Pin.OUT)
red_led = Pin(RED_LED_PIN, Pin.OUT)
servo_pwm = PWM(Pin(SERVO_PIN))
servo_pwm.freq(50)
# --- Secret Tap Pattern ---
# 1 = short delay, 2 = long delay. This is for tap, (short), tap, (long), tap
secret_pattern = [1, 2]
pattern_length = 3 # Total number of taps required
# --- Timing Thresholds (in milliseconds) ---
SHORT_DELAY_MAX = 400
LONG_DELAY_MIN = 500
LONG_DELAY_MAX = 1500
SEQUENCE_TIMEOUT = 3000
# --- State Variables ---
tap_count = 0
last_tap_time = 0
last_sensor_state = 0
# --- Helper Functions ---
def set_servo_angle(angle):
duty = ((angle / 180) * (8350 - 1350)) + 1350
servo_pwm.duty_u16(int(duty))
def reset_sequence():
global tap_count
set_servo_angle(1) # Lock
red_led.low()
green_led.high() # Ready state
tap_count = 0
print("Ready for new sequence.")
def success_sequence():
print("ACCESS GRANTED!")
green_led.low()
for i in range(5):
green_led.high(); sleep_ms(100)
green_led.low(); sleep_ms(100)
set_servo_angle(90) # Unlock
sleep_ms(5000)
reset_sequence()
def fail_sequence():
print("ACCESS DENIED!")
green_led.low()
for i in range(3):
red_led.high(); sleep_ms(250)
red_led.low(); sleep_ms(250)
reset_sequence()
# --- Initial State ---
reset_sequence()
# --- Main Loop ---
while True:
current_sensor_state = touch_sensor.value()
# Check for a new tap (a rising edge from 0 to 1)
if current_sensor_state == 1 and last_sensor_state == 0:
current_time = ticks_ms()
if tap_count == 0: # First tap
print("Sequence started...")
last_tap_time = current_time
tap_count = 1
else: # Subsequent taps
interval = ticks_diff(current_time, last_tap_time)
tap_type = 0
if interval < SHORT_DELAY_MAX: tap_type = 1 # Short
elif interval > LONG_DELAY_MIN and interval < LONG_DELAY_MAX: tap_type = 2 # Long
if tap_type == secret_pattern[tap_count - 1]:
print(f"Correct tap {tap_count}")
last_tap_time = current_time
tap_count += 1
else:
fail_sequence()
# Check for success
if tap_count == pattern_length:
success_sequence()
# Check for timeout
if tap_count > 0 and ticks_diff(ticks_ms(), last_tap_time) > SEQUENCE_TIMEOUT:
print("Sequence timed out.")
fail_sequence()
last_sensor_state = current_sensor_state
sleep_ms(20)
Rising Edge Detection - The logic if current_sensor_state == 1 and last_sensor_state == 0: is crucial. It ensures the code only registers the exact moment your finger first touches the sensor, preventing a long touch from being counted multiple times.
ticks_ms() and ticks_diff() - These are MicroPython's robust tools for measuring time intervals, which are perfect for checking the rhythm of the taps.
State Management - The tap_count variable is the core of the state machine, keeping track of how far along the user is in the secret sequence.
secret_pattern list - Stores the secret rhythm. 1 represents a short pause between taps, and 2 represents a long pause.
ticks_ms() and ticks_diff() - These are MicroPython's robust tools for measuring time intervals, which are perfect for checking the rhythm of the taps.
State Management - The tap_count variable is the core of the state machine, keeping track of how far along the user is in the secret sequence.
secret_pattern list - Stores the secret rhythm. 1 represents a short pause between taps, and 2 represents a long pause.